In an increasingly connected world, countries are engaging with global markets more than ever before. As a result, global wealth is shifting towards emerging markets. This megatrend—a global trend with sustained impacts—is profoundly influencing everyday life, society, and business.
Shifting Economic Power
Today’s infographic from iShares by BlackRock explains how emerging markets are classified, along with which countries are growing the fastest—and how investors can follow the money.
What Is An Emerging Market?
Every economy goes through five distinct stages of growth:
Pro: Greater return potential, growing middle class, increasing consumption Risk: Political instability, lack of infrastructure, lack of market access
Between 2000–2018, emerging markets’ share of global wealth has more than doubled from 10% to 24%. China is a major player in this transformation. Emerging markets fall into the transitory stages between ‘Take-off’ and ‘Drive to maturity’ as their economies modernise. Today, such countries offer lots of promise, but also come with a range of challenges:
China’s Economic Might
China’s impressive trajectory from agricultural economy to global superpower cannot be ignored. The nation is on track to overtake the U.S. in terms of gross domestic product (GDP, nominal) by the year 2030. China’s enormous growth has a ripple effect on its GDP composition. A more affluent middle class is buying higher-priced discretionary goods—such as cars and electronics—boosting the country’s domestic consumption. Investors must keep an eye out for other emerging markets that are emulating China’s example.
One Piece Of the Puzzle
China is just one case study—several other economies are also making strides on the world stage. Each country brings unique advantages, but also barriers to overcome. Source: Global Finance Magazine With these major emerging markets in mind, how can investors tap into the global wealth shift?
Where Are the Opportunities?
There are several avenues for an investor to play into this megatrend: structural solutions, consumer goods, and international investment.
Structural solutions
Emerging markets are increasingly gaining access to technology. Growth in connectivity is closely linked with improved productivity, and many countries are ripe for a surge in online users. However, much can still be done to speed up technological adoption, such as boosting 3G/4G network volume and coverage, and lowering the cost of data and smartphones to be more economical. By helping solve some of these structural constraints through technological innovation, investors can tap into the economic growth of emerging markets.
Consumer goods
As disposable income increases, a sizeable middle class will seek out products that elevate the quality of life. In India, domestic consumption is estimated to hit $6 trillion by 2023—four times its 2018 level. The region’s spending will likely be propelled by higher-priced goods, as well as a wider variety of choices across food, transport, and fitness categories. Global brands that plan to expand into emerging markets, or companies with a proven track record in these areas, are potential winners for investment.
International investment
Last but not least, investors can identify local winners in emerging wealth markets, through active or passive investing. An active investment strategy would be to directly buy into individual company stocks, listed on a country’s stock exchange. Meanwhile, a passive investing strategy would be to seek out exchange-traded funds (ETFs) covering specific markets, and/or sectors within emerging markets. Many of these are also listed on major exchanges. Diversifying either or both strategies across two or more countries can help mitigate risk. Investors can also choose index funds that broadly encompass all emerging markets. As countries climb the economic ladder, the emerging wealth shift continues to gain momentum. By staying attuned to these macro changes, investors may unlock long-term growth from emerging markets. on A statement that is as profound as it is banal. In other words, when we do history, we’re a bit like tourists. If we really want to understand the past, we have to think like a local. The infographic above, Aspects of Principal Exports of Chinese Goods to Foreign Countries, is the first in a series that we’re calling Vintage Viz, which presents a historical visualization along with the background and analytical tools to make sense of it. Today, the People’s Republic of China is the second largest economy in the world, a permanent member of the UN Security Council, and a growing military power. But at the dawn of the 20th century, things were much, much different.
Opium and the Opening of China to the West
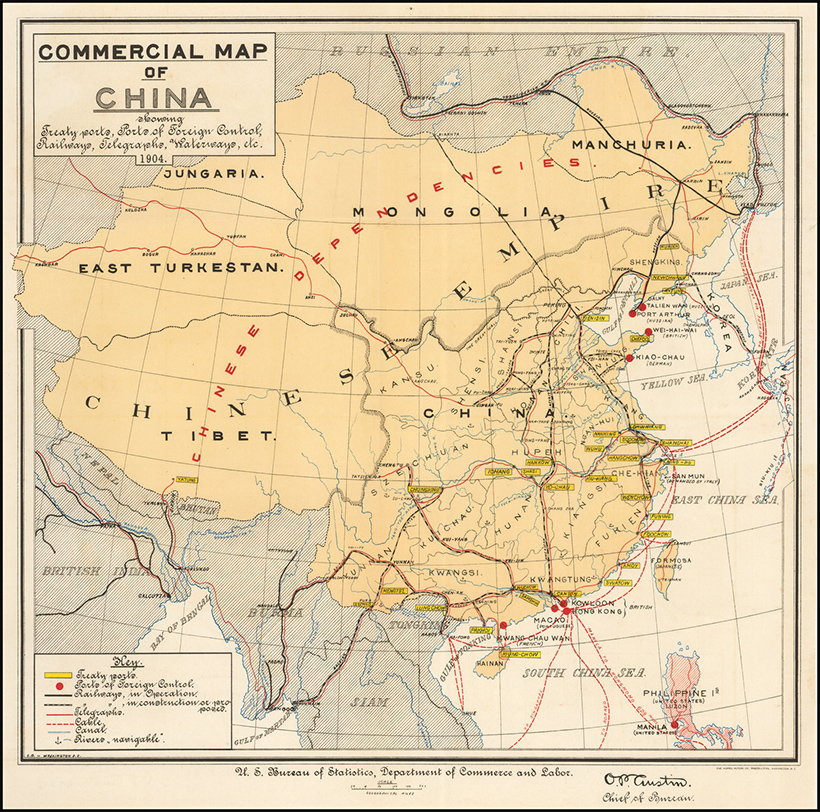
Early Sino-Western trade was restricted by the Qing emperors to three ports, and after 1757, just one, in what became known as the Canton System. This name came from the one remaining port city of the same name, present-day Guangzhou. Foreign trade was tightly monitored and subject to stiff tariffs, and Western traders chafed under these restrictions. So when in 1839, Chinese authorities moved to shut down opium smuggling—an important source of profit for foreign merchants—Western powers saw their chance and used the pretext to revise the terms of trade by force. In what became known as the Opium Wars, 1839-1842 and 1856-1860, first Great Britain and then an Anglo-French alliance defeated imperial China and imposed punitive treaties that included indemnities and lowered tariffs, but also expanded the number of ports open to foreign traders, first to five and by 1911, to more than 50.
Westerners were exempted from local laws, Christian missionaries were allowed to proselytize freely, and the opium trade was legalized. Hong Kong was also ceded to Great Britain at this time. The Treaty Port Era, also known as the Century of Humiliation, was perhaps too much for the country to bear. The weakened central government was beset by popular unrest, including the Taiping Rebellion (1850–64), which killed 20 million people, and the Boxer Rebellion (1899-1901), so-named for the secret society that led the movement, the Righteous and Harmonious Fists. Eventually, the last Chinese emperor was deposed and a republic declared in 1911. Nevertheless, the government was too weak to impose its will, and was repeatedly challenged by warlords. So as we approach the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, and the period covered by our visualization, we find China weakened internally by civil strife, and externally by Western powers.
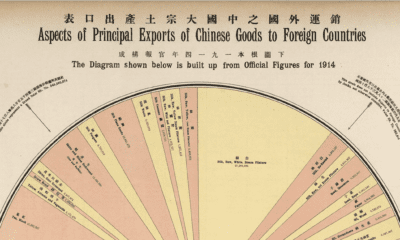
The History of this Century-Old Pie Chart
Aspects of Principal Exports of Chinese Goods to Foreign Countries captures Chinese exports for 1914, and comes from The New Atlas and Commercial Gazetteer of China: A Work Devoted to Its Geography & Resources and Economic & Commercial Development. Originally published in 1917 and edited by Edwin J. Dingle for the Far Eastern Geographical Establishment, the volume contains a wealth of data for the period. According to the book’s Preface, it “seeks to give all the information that is essential to the business-man in regard to a country… about which less is known than in regard to any similar area in the world.” The visualization breaks down total Chinese exports for 1914 in haikwan taels (hk. tls.), a unit of silver currency used to collect tariffs. In 1907, one haikwan tael was worth $0.79 U.S. dollars. Official figures come from the Chinese Maritime Customs Service. This was set up by foreign consuls after the First Opium War to collect tariffs to guarantee the payment of treaty indemnities. Exports in 1914 represented 345 million hk. tls., a 14.4% decrease from 1913, likely owing to the outbreak of the First World War that same year. Apart from “Other Metals and Minerals, Sundries, etc,” which served as a catch-all category, the largest categories were silks and teas of various types, representing 22.6% and 10.4% of total exports respectively. Below are some more details that emerge from this visualization.
All the Tea in China
The Chinese tea trade was the subject of another visualization in the Atlas. It shows that China had been steadily losing ground to British India. Between 1888-1892 Chinese exports to Great Britain were 242 million pounds against India’s 105 million pounds. By 1912-1913, India had surpassed China to export 279 million pounds against 198 million pounds. In 1914, the majority of Chinese exports went to Russia, 902,716 piculs in all. A picul is equal to “as much as a man can carry on a shoulder-pole” or about 133 pounds.
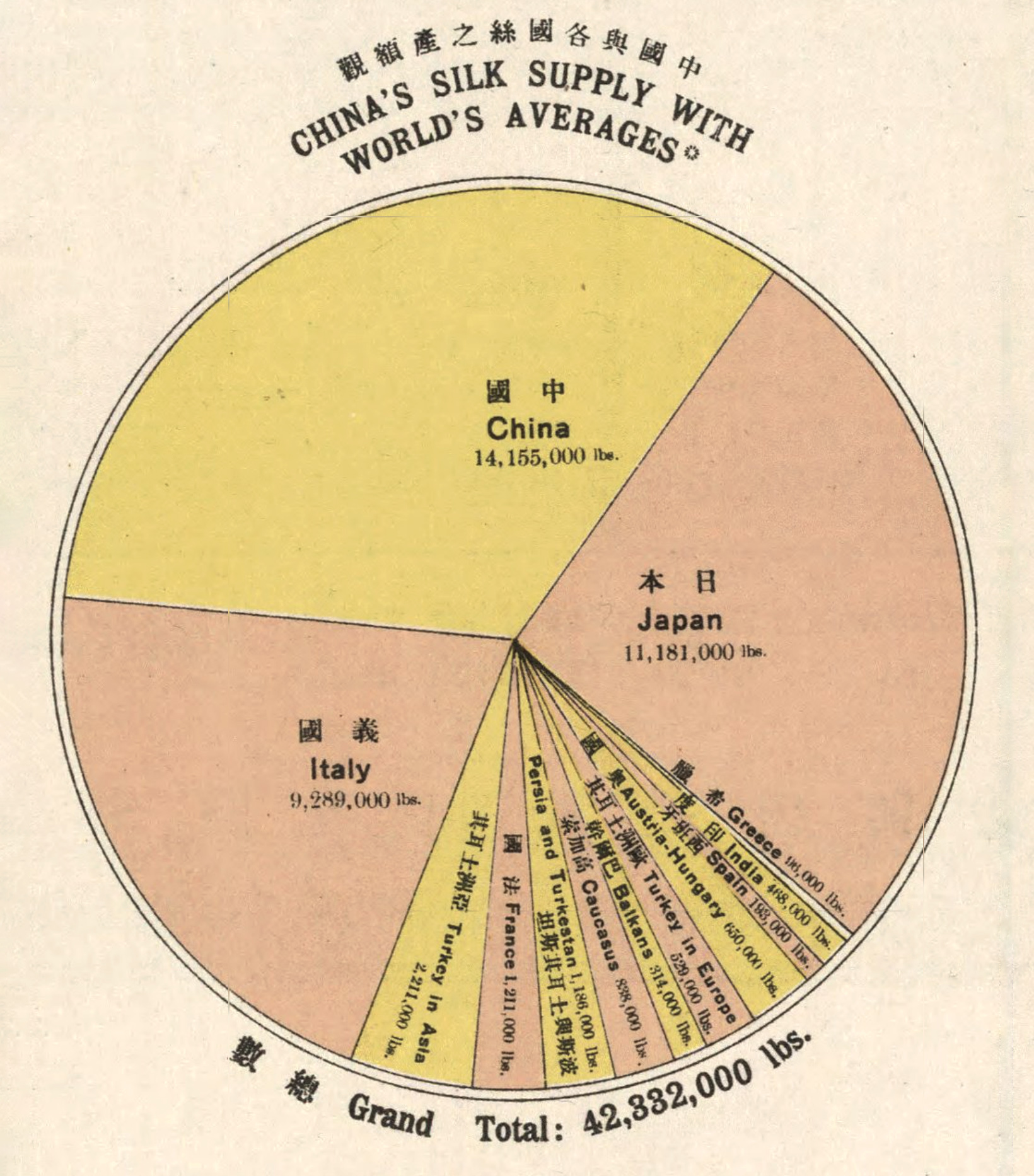
The Silk Road to Profits
Silk has long been in demand in the West as a luxury good, giving its name to the overland trade route that connected East and West for centuries: the Silk Road. In 1914, China was the largest producer and exporter of silks in the world. On an annual basis, China averaged 14 million pounds, compared to the number two spot, Japan, at 11 million pounds, and number three, Italy, at 9 million pounds. Together, these three controlled 81.7% of the global silk trade.
The Opium of the Masses?
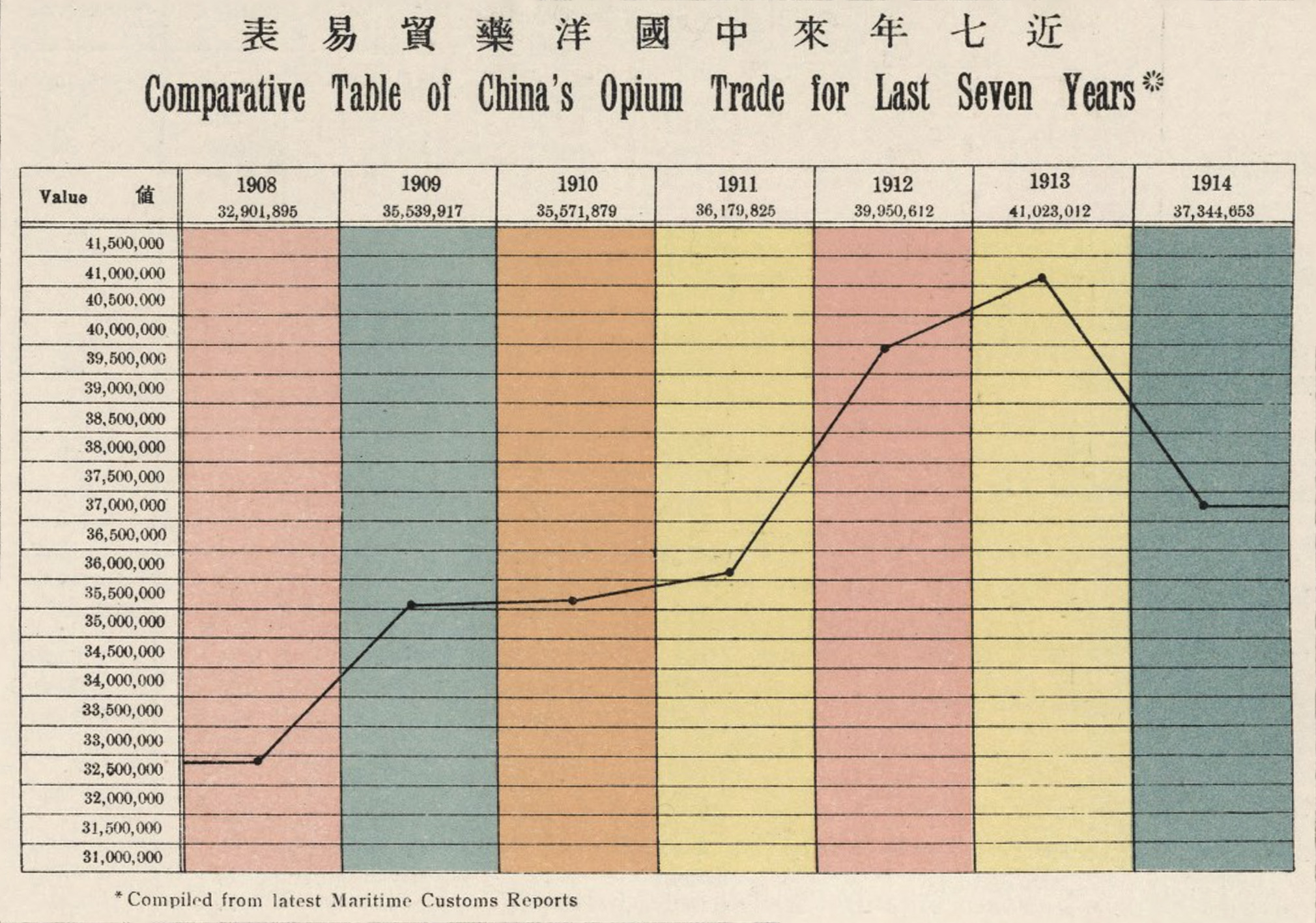
The opium trade, the pretext that opened China to foreign trade, was still big money in 1914. A total of 37 million hk. tls. were imported in 1914 from India, up 11.9% from 1908. This is actually down from a peak of 41 million hk. tls. in 1913.
In 1907, China signed the Ten Year Agreement with India, which ultimately phased out the opium trade. By 1917 the trade was all but extinguished.
Back to the Future
The Aspects of Principal Exports of Chinese Goods to Foreign Countries is a far cry from the contemporary trade picture. China’s top export in 2021 was in the category “telephones for cellular networks or other wireless networks,” and was worth $147.1 billion. But it’s worth noting that China today is a direct result of this period. The resentment created during the Century of Humiliation would eventually help lead to Mao Zedong, the Long March, and the establishment of the People’s Republic of China. And in 1979, the Chinese central government would set up the first of their own “treaty ports,” in the form of special economic zones, places where foreign companies could set up shop. But this time, it wasn’t foreign powers who were making the rules.