That’s because at the beginning of such a phenomenon, the quantities involved can seem insignificant. One becomes two, two becomes four, and so on. But if the environment is right, and the growth continues on, it can all of a sudden take over. This growth can lead to a paradigm shift and a new status quo, as well as massive opportunities along the way.
The Water Droplet Analogy
One famous example of exponential growth is the water droplet and stadium analogy. Imagine a giant football stadium, and you are sitting in the very highest seat. You can see the whole field. In the middle of the stadium, there are drops of water falling at an increasing rate. In the first minute a single drop of water falls, in the second minute there are two drops of water added, and in the third minute, there are four drops of water, and so on. The rate doubles each minute. When do you think the stadium is full of water? Does it take hours, days, or weeks? For the first 30 minutes, not much seems to happen – there is a growing puddle, but it’s not likely something you can see from the very top seat. After 45 minutes the stadium is still 93% empty – but by 49 minutes, the entire stadium is full of water (and you’re swimming)!
The Electric Vehicle Market
Today’s infographic comes to us from Raconteur, and it helps visualize anticipated growth in the electric vehicle market – a segment that sits at 1-2% of total vehicle sales currently. Using projections from Morgan Stanley, it shows that electric vehicle sales are expected to surpass those of traditional vehicles by 2038, while the global fleet of EVs is expected to surpass one billion by 2047. Meanwhile, the transition to electric will be a game-changer for carmakers. Morgan Stanley’s analysis sees the average profitability of combustion engine models falling through the early 2020s, eventually turning to a loss per unit by 2028. On the flipside, negative profit margins for electric vehicles will peak in 2023 as production continues to ramp, and EV making will switch to a profitable business by 2029.
An EV Flood?
Will we wake up one morning with the auto market being flooded with new EVs, like in the aforementioned water drop analogy? Certainly not. Manufacturing processes are notoriously difficult to scale, and we still need to source the raw materials needed to fuel the green revolution. However, the speed of the transition to electric vehicles will still be surprising to many detractors – and for now, barring an unexpected drop in the price of oil to below $30/bbl, there doesn’t seem to be any obstacle that will slow the adoption of EVs. on
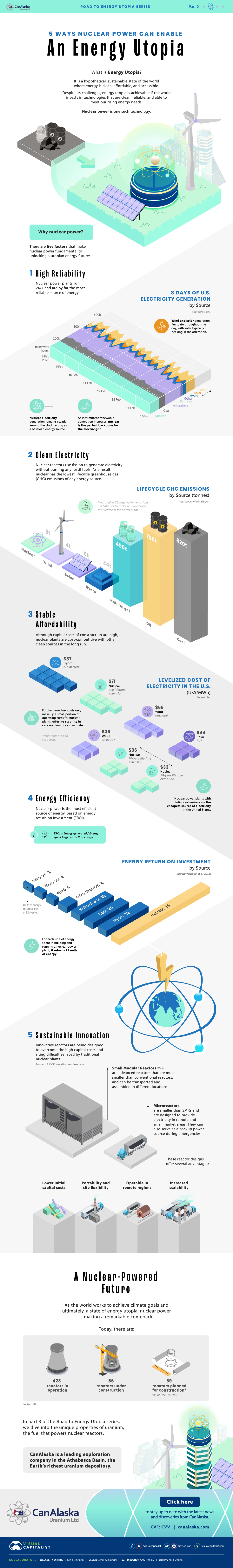
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
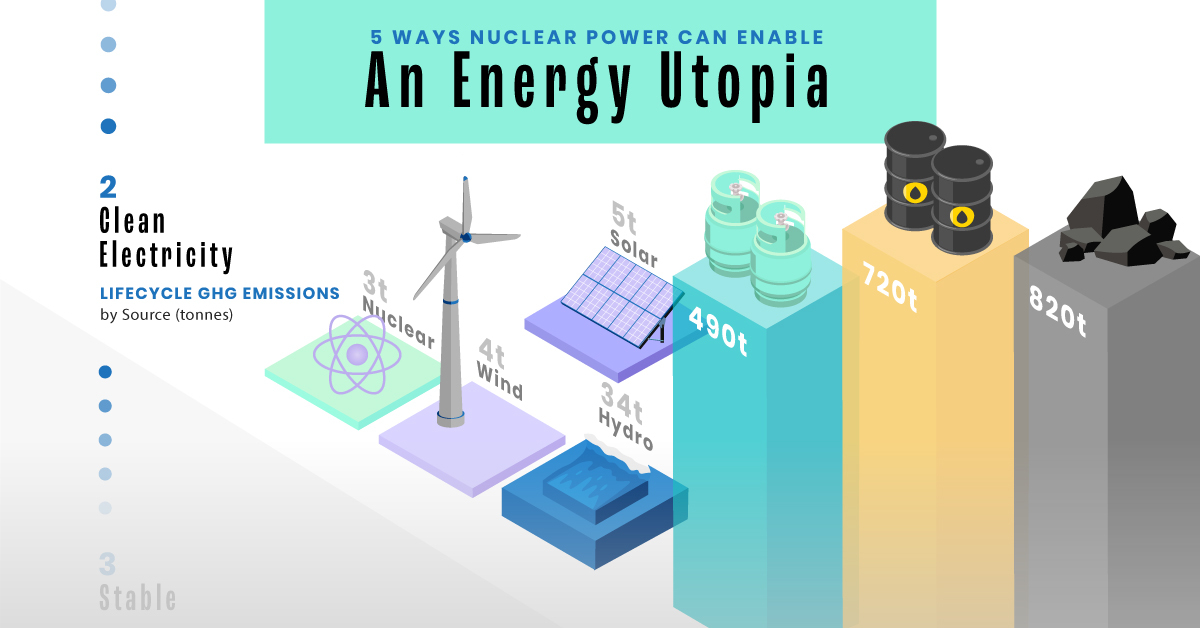
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.