R&D spend is also casting a wider global net. In 1960, the U.S. made up nearly 70% of global R&D spending, and by 2020 this had fallen to 30%. From job creation and public health to national security and industrial competitiveness, R&D plays a vital role in a country’s economic growth and innovation, impacting nearly every corner of society—either directly or indirectly. Along with R&D spend, other key ingredients play an important role in driving progress and innovation. These include technological adoption, scientific research, and venture capital activity, among others. The above infographic ranks the world’s most innovative economies using data from the UN’s WIPO Global Innovation Index.
What Defines an Innovative Economy?
Innovation is inherently challenging to quantify, but the Global Innovation Index is a longstanding attempt to do just that. The framework used for the index was designed to create a more complete analysis, comprising of 81 indicators across seven categories to calculate a country’s score: As the above table shows, the framework aims to identify indicators that foster an innovative environment and breakthrough technologies. It’s worth noting that each country’s overall innovation score is a mix of these categories, and countries with similar scores can be strong in different areas.
The 50 Most Innovative Countries in 2022
Switzerland ranks at the top for the 12th year in a row—above the U.S., South Korea, and Israel. For many, this may come as a surprise. However, the country’s intellectual property rules are considered world-class, and they are complemented by strong collaboration between universities and industry. In addition, the country attracts top talent thanks to its high quality of living. Countries across Europe also feature prominently in the top 10, including Sweden (#3), the United Kingdom (#4) and the Netherlands (#5). South Korea (#6), is known for its high R&D intensity. This is driven by its industrial conglomerates, known as chaebols, that are generally family-owned. Samsung and LG are among its largest companies, known for their high degree of corporate-academic collaboration. Below, we will take a closer look at the most innovative countries by region.
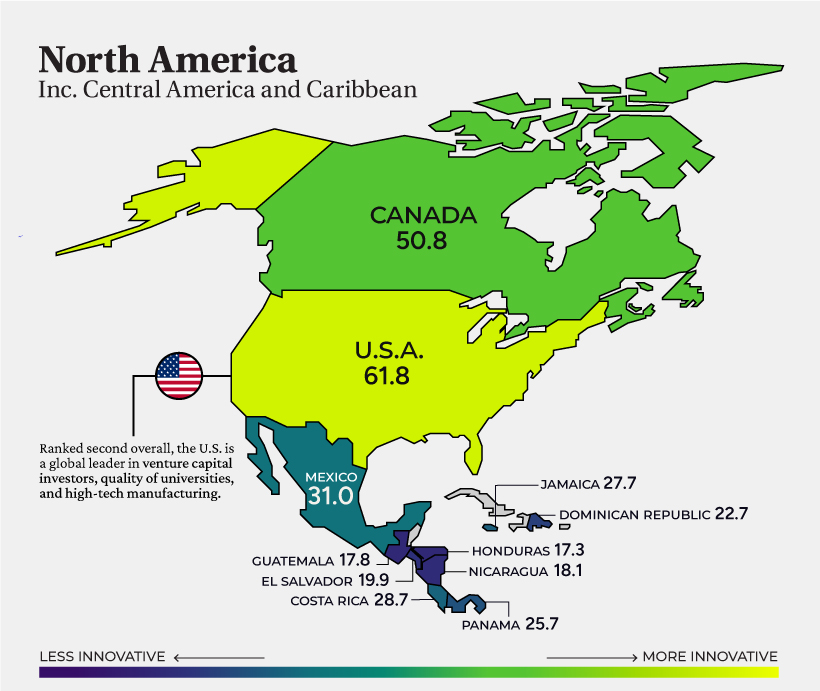
North America
In North America, the U.S. ranks highest. The country has long been known as a global leader in innovation, with a strong track record of introducing new ideas and technologies that have transformed the way we live and work. The U.S. ranks #1 in a number of indicators, including university-industry R&D collaboration and intangible asset intensity. Ranking second in the region is Canada (Global rank: #15). Across all countries, it ranks first on measures of joint venture and strategic alliances per billion dollars of GDP (PPP) and number of venture capital (VC) recipients per billion dollars of GDP (PPP). In 2021, VC investment topped $14.7 billion across 752 deals.
Another interesting example is Honduras (#113). Driving innovation in the country is a new economic zoning experiment called Zones for Economic Development and Employment (ZEDEs). To date, these zones have attracted about a quarter of a billion dollars in private investment funding and have created thousands of new jobs.
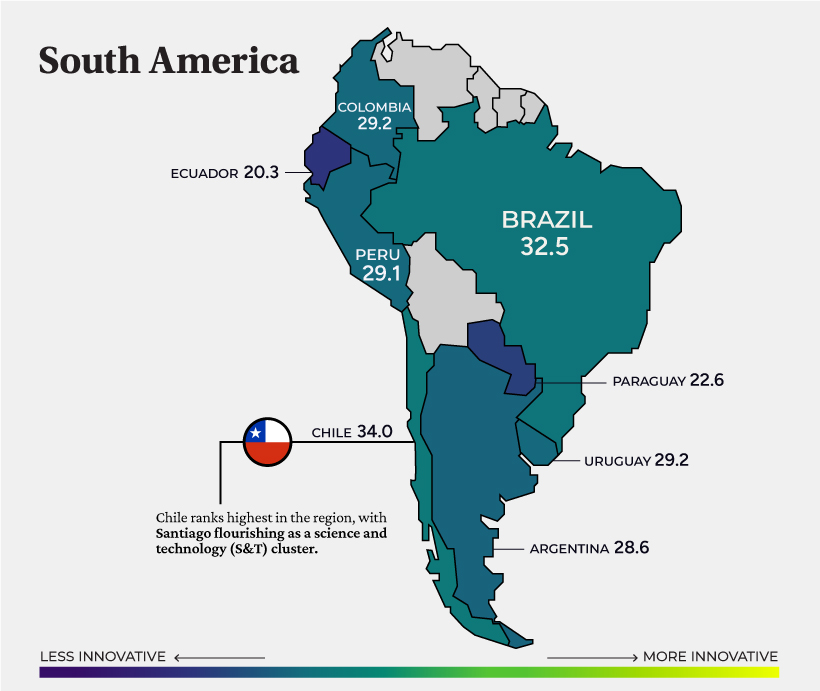
South America
Chile (#50) ranks first across the region, thanks to its promising tech sector. To date, it is home to an estimated 8,000 tech companies. The country also has the highest scale of mobile connectivity in the region. In late 2021, it launched the first 5G network in South America.
Following Chile is Brazil (#54), which saw a record number of IPOs in 2021 that were valued at nearly $7 billion.
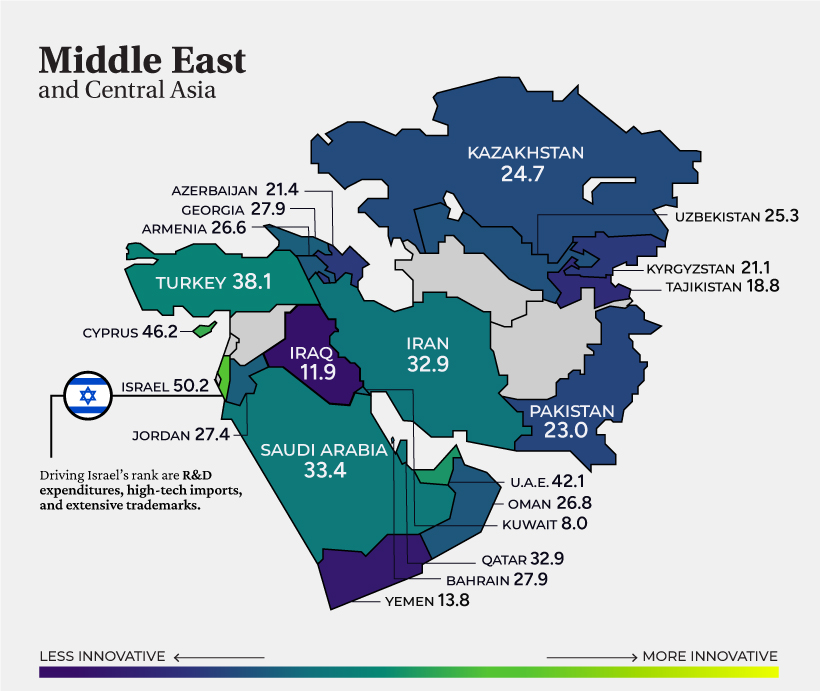
Middle East and Central Asia
As the highest ranked in the region, Israel (#16) is the sole country globally that spends over 5% of GDP on R&D. Overall, it is a global leader in patent applications and information and communication technology (ICT) services exports. For context, the country’s density of start-ups per capita is 16 times that of Europe.
The small island nation of Cyprus (#27) follows in second, supported by government funding focused on start-ups. Meanwhile, Turkey (#37) in fourth, is home to six unicorns*, fostered by its development of a megatech corridor through Istanbul to Izmir. *A unicorn is a privately-held startup that has a valuation of over $1 billion.
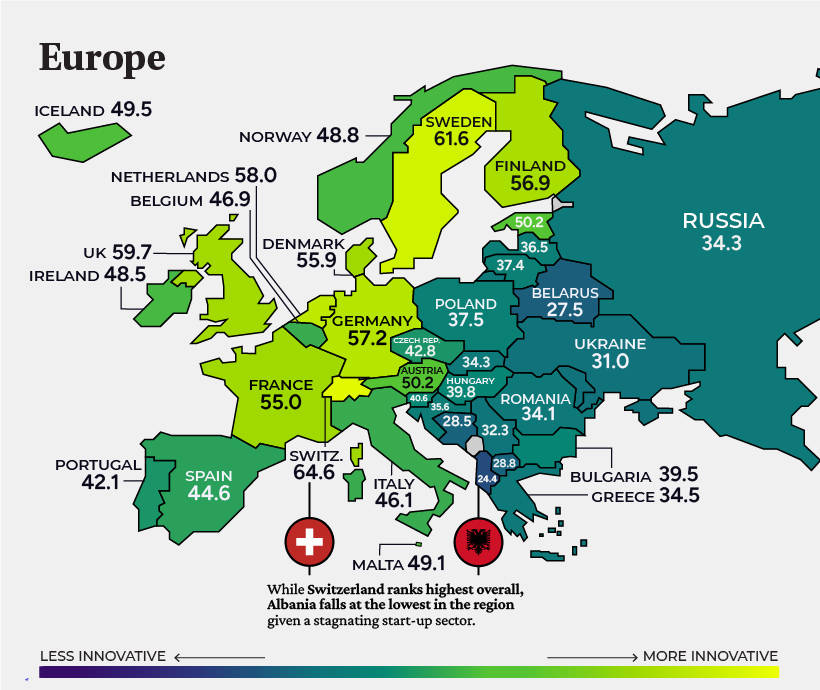
Europe
With 15 of the top 25 economies in the world, Europe is a powerhouse for fostering innovative ecosystems. The continent is also a leader in social progress, equality, and life satisfaction. The region scores 30 on inequality according to the Gini Index compared to 41 for America. For many, technological output isn’t the first thing that comes to mind when they think of Europe, but VC deals surged over 53% in 2021. London, Berlin, and Paris were leading cities for VC activity.
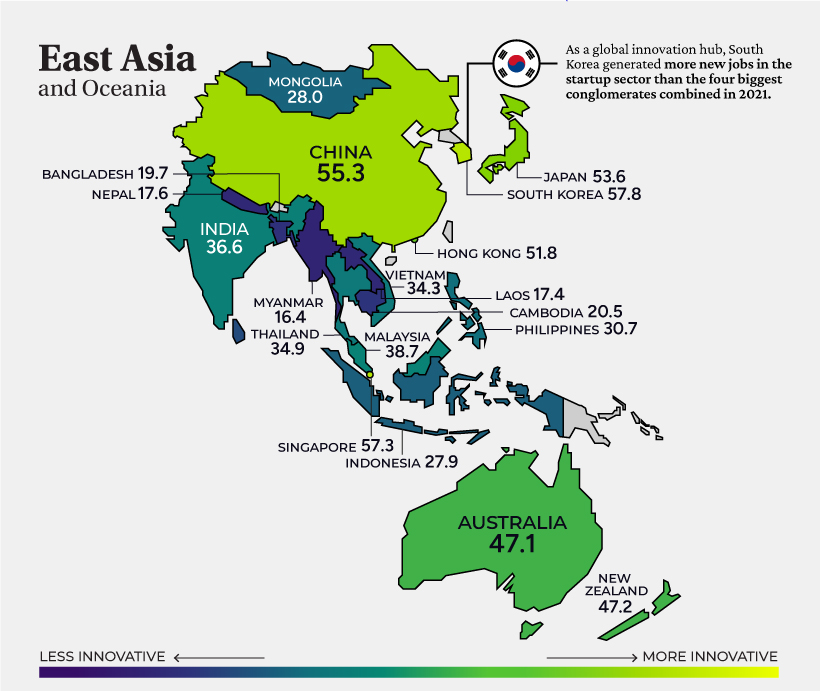
East Asia and Oceania
South Korea (#6) ranks highest across East Asia and Oceania, and has established itself as a leader in technology and innovation on the global stage. Through its New Deal initiative, the government is spearheading projects on smart healthcare, AI, and smart industrial complexes. At the same time, it is accelerating the construction of eco-friendly infrastructure and renewable energy. South Korea’s Hyundai and its subsidiary Kia have made considerable ground in electric vehicle (EV) production, comprising 9% of the U.S. EV market, the second-highest share after Tesla.
China sits just outside the global top 10, and now ranks #1 in multiple indicators, including labor productivity growth and trademarks by origin. China’s economic output per employed worker increased an impressive 4.2% annually from 2011 to 2019, on average.
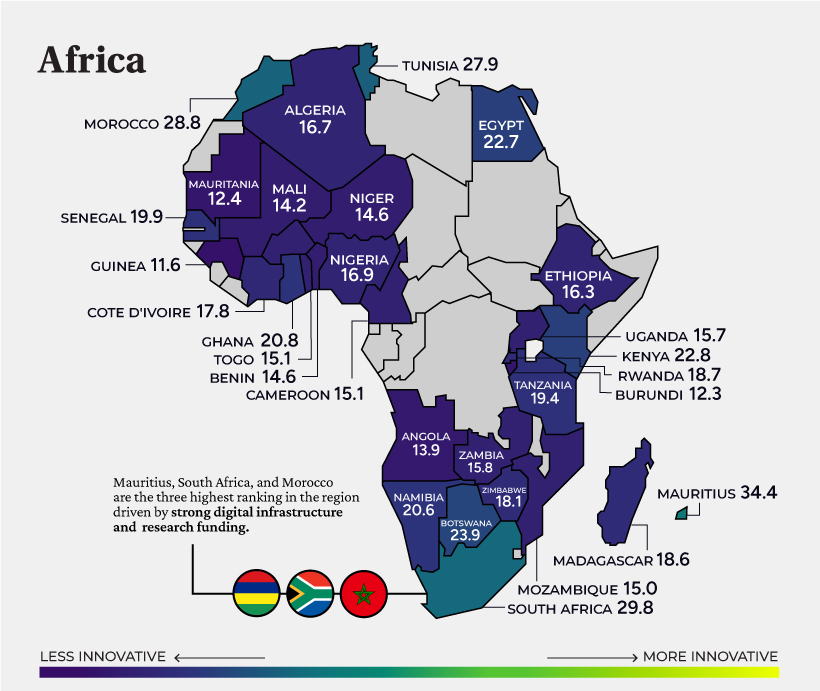
Africa
The highest ranked in Africa is the island nation of Mauritius (#45). Underscoring its rank is the strength of its institutions and market sophistication. Meanwhile, the government is accelerating investment in tech incubators, research-business collaboration, and tax incentives for R&D investment.
Panasonic opened their headquarters in Cape Town in 2018. Oracle, IBM, Google, and Microsoft also have offices in the country’s expanding tech hub. on But fast forward to the end of last week, and SVB was shuttered by regulators after a panic-induced bank run. So, how exactly did this happen? We dig in below.
Road to a Bank Run
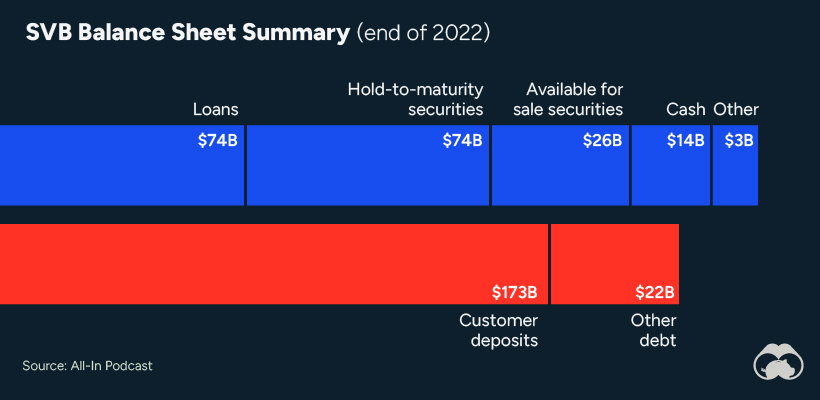
SVB and its customers generally thrived during the low interest rate era, but as rates rose, SVB found itself more exposed to risk than a typical bank. Even so, at the end of 2022, the bank’s balance sheet showed no cause for alarm.
As well, the bank was viewed positively in a number of places. Most Wall Street analyst ratings were overwhelmingly positive on the bank’s stock, and Forbes had just added the bank to its Financial All-Stars list. Outward signs of trouble emerged on Wednesday, March 8th, when SVB surprised investors with news that the bank needed to raise more than $2 billion to shore up its balance sheet. The reaction from prominent venture capitalists was not positive, with Coatue Management, Union Square Ventures, and Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund moving to limit exposure to the 40-year-old bank. The influence of these firms is believed to have added fuel to the fire, and a bank run ensued. Also influencing decision making was the fact that SVB had the highest percentage of uninsured domestic deposits of all big banks. These totaled nearly $152 billion, or about 97% of all deposits. By the end of the day, customers had tried to withdraw $42 billion in deposits.
What Triggered the SVB Collapse?
While the collapse of SVB took place over the course of 44 hours, its roots trace back to the early pandemic years. In 2021, U.S. venture capital-backed companies raised a record $330 billion—double the amount seen in 2020. At the time, interest rates were at rock-bottom levels to help buoy the economy. Matt Levine sums up the situation well: “When interest rates are low everywhere, a dollar in 20 years is about as good as a dollar today, so a startup whose business model is “we will lose money for a decade building artificial intelligence, and then rake in lots of money in the far future” sounds pretty good. When interest rates are higher, a dollar today is better than a dollar tomorrow, so investors want cash flows. When interest rates were low for a long time, and suddenly become high, all the money that was rushing to your customers is suddenly cut off.” Source: Pitchbook Why is this important? During this time, SVB received billions of dollars from these venture-backed clients. In one year alone, their deposits increased 100%. They took these funds and invested them in longer-term bonds. As a result, this created a dangerous trap as the company expected rates would remain low. During this time, SVB invested in bonds at the top of the market. As interest rates rose higher and bond prices declined, SVB started taking major losses on their long-term bond holdings.
Losses Fueling a Liquidity Crunch
When SVB reported its fourth quarter results in early 2023, Moody’s Investor Service, a credit rating agency took notice. In early March, it said that SVB was at high risk for a downgrade due to its significant unrealized losses. In response, SVB looked to sell $2 billion of its investments at a loss to help boost liquidity for its struggling balance sheet. Soon, more hedge funds and venture investors realized SVB could be on thin ice. Depositors withdrew funds in droves, spurring a liquidity squeeze and prompting California regulators and the FDIC to step in and shut down the bank.
What Happens Now?
While much of SVB’s activity was focused on the tech sector, the bank’s shocking collapse has rattled a financial sector that is already on edge.
The four biggest U.S. banks lost a combined $52 billion the day before the SVB collapse. On Friday, other banking stocks saw double-digit drops, including Signature Bank (-23%), First Republic (-15%), and Silvergate Capital (-11%).
Source: Morningstar Direct. *Represents March 9 data, trading halted on March 10.
When the dust settles, it’s hard to predict the ripple effects that will emerge from this dramatic event. For investors, the Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen announced confidence in the banking system remaining resilient, noting that regulators have the proper tools in response to the issue.
But others have seen trouble brewing as far back as 2020 (or earlier) when commercial banking assets were skyrocketing and banks were buying bonds when rates were low.