Tokyo hosted the 2020 Summer Olympics from July 24 to August 9, 2021, marking the second time Japan has hosted the Summer Olympics. The country was first given the honor back in 1964 becoming the first Asian nation to host the Olympic Games. Even in this most challenging of climates where the games had to be pushed by a year, nothing stopped the athletes from exceeding their limits and breaking long-held records.
The Final 2020 Olympic Medal Count
In a complete show of dominance, the U.S. won the most medals at the Olympics, raking in 113 total with 39 gold medals. The U.S. beat out China to claim the top spot by a single gold medal. China finished the games with an impressive 88 medals in total. The host country Japan comes in at third with 27 gold medals and a total of 58 medals. Here is the final Olympic medal count for each country that participated in the Tokyo Olympic Games: Of course, countries with larger populations have an inherent advantage, so it’s also interesting to look at the top countries by population per medal. By this measure, the European microstate of San Marino comes out on top. This was San Marino’s first ever medal showing at an Olympic Games. Turkmenistan and Burkina Faso also won medals for the first time at Tokyo 2020. Here’s a look at the top 15 countries by population per Olympic medal: Among countries with a slightly larger population, the Netherlands and Australia had strong showings.
Other Facts and Figures About the 2020 Tokyo Olympics
Despite a year-long delay and a slew of challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, this unprecedented Olympic Games went ahead. Here are 12 interesting things to note about the 2020 Tokyo Olympics: The Olympic Torch Relay traveled through all 47 of Japan’s prefectures over 121 days. It involved 10,500 torchbearers, who ultimately arrived at Japan’s Olympic Stadium in Tokyo. 40 venues in and around the city of Tokyo hosted 33 Olympic Sports and 22 Paralympic Sports events. The two main areas were the Heritage Zone and the Tokyo Bay Zone. The Tokyo Olympics were the most expensive Olympics on record. According to officials, the budget for the Games was $15.4 billion. On the other hand, Japanese government auditors have claimed the total spending topped $20 billion. This is almost three times the original forecast of around $7.4 billion when Tokyo put together its bid for the Olympics. The postponement of the Games cost the country close to $2 billion, after initial speculation that the cost could be as high as $6 billion. 29 athletes qualified as part of the IOC Refugee Olympic Team for the Tokyo Olympic Games. Rio 2016 was the first time that an IOC refugee team had made an appearance at the Olympic games. Syrian table tennis player Hend Zaza and Japanese skateboarder Kokona Hiraki were the youngest athletes in Tokyo at 12 years old, while Australian equestrian Mary Hanna was the oldest at 66 years old. Athletes at the Tokyo Olympics put their medals around their own necks to protect against spreading COVID-19. After being presented medals on a tray, the athletes picked it up and medalled themselves. There would also be no handshakes or hugs at the podiums. To promote sustainability, this year’s Olympics repurposed a number of the venues used in the 1964 Games. Moreover, the podiums, uniforms, medals, and even the beds at the Olympic Village were all made from recycled materials. While Japan is not the first to make Olympic medals from recycled materials, it is the first time that citizens of a host country proactively donated their electronic devices as materials for the medals. This year, the Games nearly reached gender parity. According to the IOC, of the almost 11,000 Olympic athletes in Tokyo, nearly 49% were women, marking the first “gender-balanced” games in its history. Nearly 85 years after the canoe sprint made its Olympic debut, the women’s sprint event was added to the Olympic games this year. Weightlifter Laurel Hubbard from New Zealand was the first openly transgender woman competing in any event at the Olympics. She joined other elite athletes like footballer Quinn from Canada and U.S. cyclist Chelsea Wolfe to participate in this year’s games. Starting with four-time grand slam champion Naomi Osaka withdrawing from the French Open over mental health concerns, the conversation about an athlete’s mental preparedness was as important as their physical one at the games. After Simone Biles stepped away from the U.S. women’s gymnastics team in the all-around contest earlier last week, numerous athletes worldwide have continued to elevate conversations surrounding mental health, especially in competitive sports. Olympic high jumpers Mutaz Essa Barshim of Qatar and Gianmarco Tamberi of Italy mutually decided to share the top spot in their event. The last time the gold medal was shared among two athletes at the Olympics was 113 years ago. Four sports made their Olympic debuts at the Tokyo Games: karate, skateboarding, sport climbing, and surfing. Other sports added new disciplines, including men’s and women’s three-on-three basketball and the BMX freestyle event. Humanoid Robots helped on the field for the first time, fetching hammers and javelins flung during field events and interacting with spectators. This was also the first time a host used facial recognition systems to provide athletes and officials venue access, helping to increase and speed up security.
Next Stop, Paris
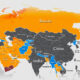
The Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games will take place from 26 July to 11 August 2024. During those weeks, Paris will be at the center of the sporting world. The IOC is keen to set a new standard for inclusive, gender-balanced and youth-centered games. The next Olympics are expected to see even more athlete and spectator participation—hopefully, one where they likely won’t have to work around COVID-19 restrictions. With numerous new sports added in Tokyo’s Olympic Games, we might even see breakdancing in the Paris version of events. Here’s to the next four years. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.