That said, from a purely economic angle, researchers can and do examine these things—as well as economic data like unemployment and lost GDP, to assign dollar figures to the pandemic. Using data from a study out of Harvard University, these visualizations focus on putting the economic cost of COVID-19 in the U.S. in perspective. To help us understand the immense price associated with a pandemic, the study looked at other comparables like the costs of running America’s longstanding war on terror.
The Cost of COVID-19
Since the pandemic took hold in the U.S. in March 2020, job loss has been one of the most significant consequences. Unemployment claims in the U.S. have recently reached a total of 60 million, while lost GDP is estimated to be around $7.6 trillion. Unemployment, uncertainty, lost loved ones, and lost social connections, have led to spikes in depression and anxiety. In April 2020, around 40% of U.S. adults reported having at least one of these mental illnesses. Based on the sheer number of people struggling, the cost of mental health impairment could be as high as $1.6 trillion, according to these researchers. The economic value of a human life can be put in terms of ‘statistical lives’, a notion used in both American and global health policy. While human life is priceless, the value tied to one using this metric sits between $7-$10 million. Even when using the lower end of the scale, the cost of premature death due to COVID-19 is estimated to be $4.4 trillion. Finally, when looking at the long-term healthcare costs that could impact people who contract COVID-19, the price comes out to almost $2.6 trillion. These costs will go on for decades as certain lifelong conditions can emerge out of COVID-19, like respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Many of these conditions could also end up causing premature deaths, drawing out the total cost of COVID-19 even further.
The Cost of War
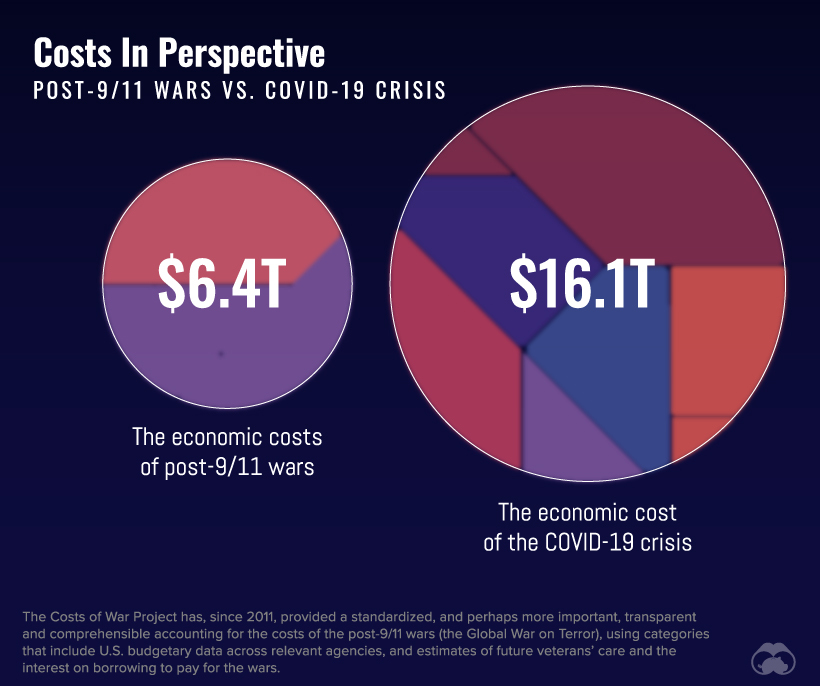
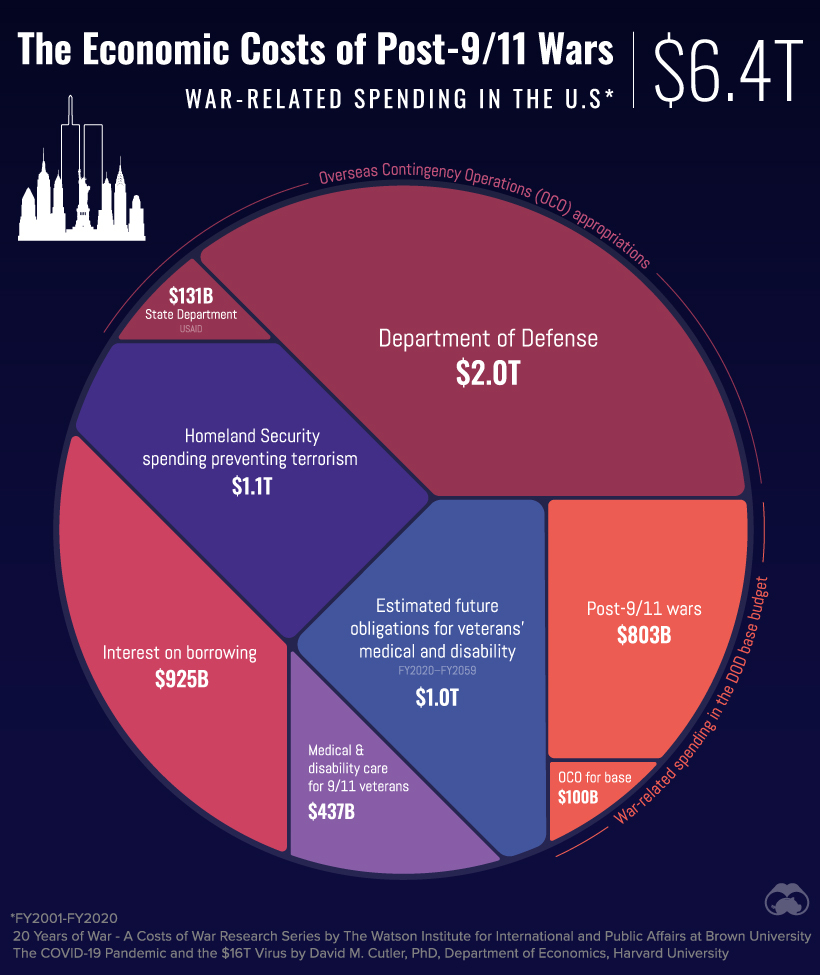
Both a global pandemic and a war have long-term health consequences and are extremely pricey. The estimated cost of the post-9/11 wars rises to over $6 trillion. This is measured by the spending of the Department of Defense, the Department of State, and USAID. The estimate also takes into consideration current and future spending on medical and disability care for veterans, the cost of war appropriations and spending, the estimated interest on borrowing for different departments, and the spending the Department of Homeland Security has done in order to prevent and respond to terrorism. Medical and disability care for veterans from the post-9/11 wars specifically comes out to $437 billion, with estimated future obligations for their care going up to $1 trillion. The increases to the Department of Defense’s budget was $803 billion thanks to the post 9/11 wars, and the Department of Homeland Security has spent more $1.05 trillion on terrorism prevention and response. While the costs associated with war are immense, and while the consequences of fighting in a war are usually lifelong, the estimated price is still about $10 trillion cheaper than the cost of COVID-19 in the United States.
Throwing Money at the Problem?
The short-term solution to COVID-19 seems to be vaccine investment, with the U.S. currently purchasing more than one billion doses. Vaccines could spell the return to a more normal life, both in terms of physical health and the health of the economy. While economic recovery is on the horizon, the U.S—and other nations around the globe—will continue to pay the cost of COVID-19 for years to come. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.