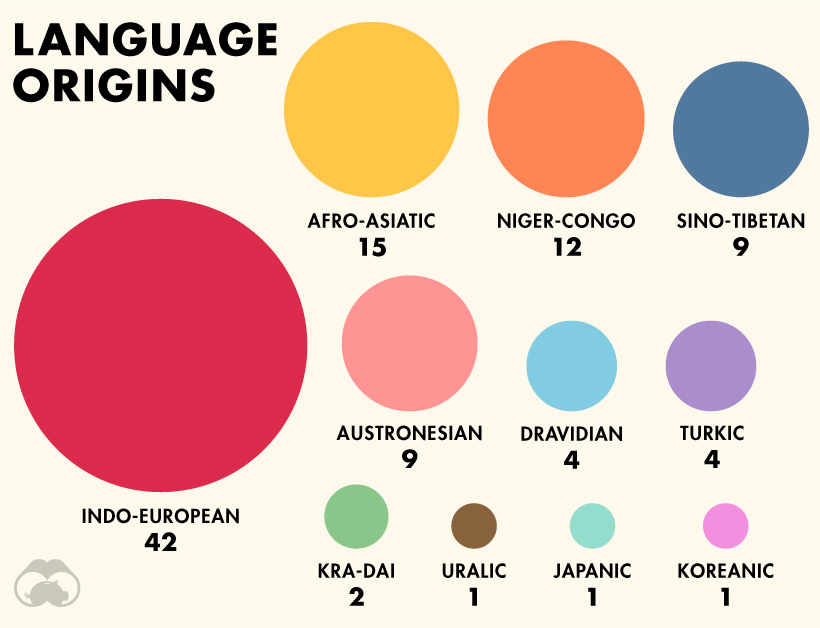
The popularity of a language depends greatly on utility and geographic location. Additionally, how we measure the spread of world languages can vary greatly depending on whether you look at total speakers or native speakers. Today’s detailed visualization from WordTips illustrates the 100 most spoken languages in the world, the number of native speakers for each language, and the origin tree that each language has branched out from.
How Do You Define A Language?
The data comes from the 22nd edition of Ethnologue, a database covering a majority of the world’s population, detailing approximately 7,111 living languages in existence today. The definitions of languages are often dynamic, blurring the lines around a singular understanding of what makes a language:
Linguistic: focused on lexical and grammatical differences, or on variations within speech communities Social: focused on cultural or political factors, as well as heritage and identity
For the purposes of measurement, the researchers use the ISO 693-3 set of criteria, which accounts for related varieties and dialects—ensuring that linguistics are not the only factor considered in this count of languages. Here are the language origins of the 100 most spoken languages:
Indo-European languages have the widest spread worldwide. According to Ethnologue, the language family contains over 3 billion speakers in total. Interestingly, there are actually 1,526 Niger-Congo languages altogether, though only 12 are represented here. Let’s now dive into the top 10 most spoken languages overall.
Which Languages Have the Most Speakers?
It comes as no surprise that English reigns supreme, with over 1.1 billion total speakers—or roughly 15% of the global population. Mandarin Chinese, Hindi, Spanish, and French round out the top five. However, this is only one piece in the full fabric of languages. The metrics for native speakers tell a slightly different tale, as Mandarin Chinese shoots up to 918 million—almost 2.5x that of English native speakers.
Here, Spanish comes in strong second for native speakers with 460 million, considering it’s well-used across Latin America. The Indian languages of Hindi and Bengali cap off the top five by native speakers as well. These are the biggest languages people learn growing up, but what about the ones they pick up later in life?
What About Second (L2) Languages?
Nearly 43% of the world’s population is bilingual, with the ability to switch between two languages with ease. From the data, second language (L2) speakers can be calculated by looking at the difference between native and total speakers, as a proportion of the total. For example, 66% of English speakers learned it as a second language. Swahili surprisingly has the highest ratio of L2 speakers to total speakers—although it only has 16 million native speakers, this shoots up to 98 million total speakers. Overall, 82% of Swahili speakers know it as a second language. Swahili is listed as a national or official language in several African countries: Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. It’s likely that the movement of people from rural areas into big cities in search of better economic opportunities, is what’s boosting the adoption of Swahili as a second language. Indonesian is another similar example. With a 78% proportion of L2 speakers compared to total speakers, this variation on the Malay language has been used as the lingua franca across the islands for a long time. In contrast, only 17% of Mandarin speakers know it as a second language, perhaps because it is one of the most challenging languages to learn.
Keeping Language Traditions Alive
Languages are fluid, and constantly evolving—altogether, the 100 most spoken languages paint a unique picture across centuries of a changing world. Here’s the full list of these languages, by types of speakers and language origin. One reason these languages are popular is that they are actively and consistently used. Unfortunately, nearly 3,000 (about 40%) of all languages are at risk of being lost, or are already in the process of dying out today. —UN, IYoIL statement As a result, the United Nations declared 2019 the International Year of Indigenous Languages (IYoIL), with a resolution to continue fostering these languages and pass on their knowledge for future generations. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.