Cotton is present in our everyday life, from clothes to coffee strainers, and more recently in masks to control the spread of COVID-19. As the most-used natural fiber, cotton has become the most important non-food agricultural product. Currently, approximately half of all textiles require cotton fibers. The above infographic lists the world’s top cotton producers, using data from the United States Department of Agriculture.
Fancy Fabric
Originating from the Arabic word “quton,” meaning fancy fabric, cotton is a staple fiber made up of short fibers twisted together to form yarn. The earliest production of cotton was around 5,000 B.C. in India, and today, around 25 million tons of cotton are produced each year. Currently, five countries make up around 75% of global cotton production, with China being the world’s biggest producer. The country is responsible for over 23% of global production, with approximately 89 million cotton farmers and part-time workers. Cotton’s importance cannot be understated, as it is the primary input for the Chinese textile industry along with many other nations’ textile industries. The United States is the leading global exporter of cotton, exporting three-fourths of its crop with China as the top buyer. Despite its importance for the global economy, cotton production faces significant sustainability challenges.
The Controversy Over Cotton
Cotton is one of the largest users of water among all agricultural commodities, and production often involves applying pesticides that threaten soil and water quality. Along with this, production often involves forced and child labor. According to the European Commission, child labor in the cotton supply chain is most common in Africa and Asia, where it comes from small-holder farmers. In 2020, U.S. apparel maker Patagonia stopped sourcing cotton from the autonomous territory of Xinjiang because of reports about forced labor and other human rights abuses against Uighurs and other ethnic minorities. L Brands, the parent company of Victoria’s Secret, has also committed to eliminating Chinese cotton from its supply chain. Whether these changes in supply chains impact China’s cotton production and its practices, cotton remains essential to materials found across our daily lives. on Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain. When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues. The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
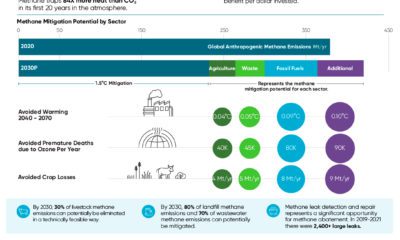
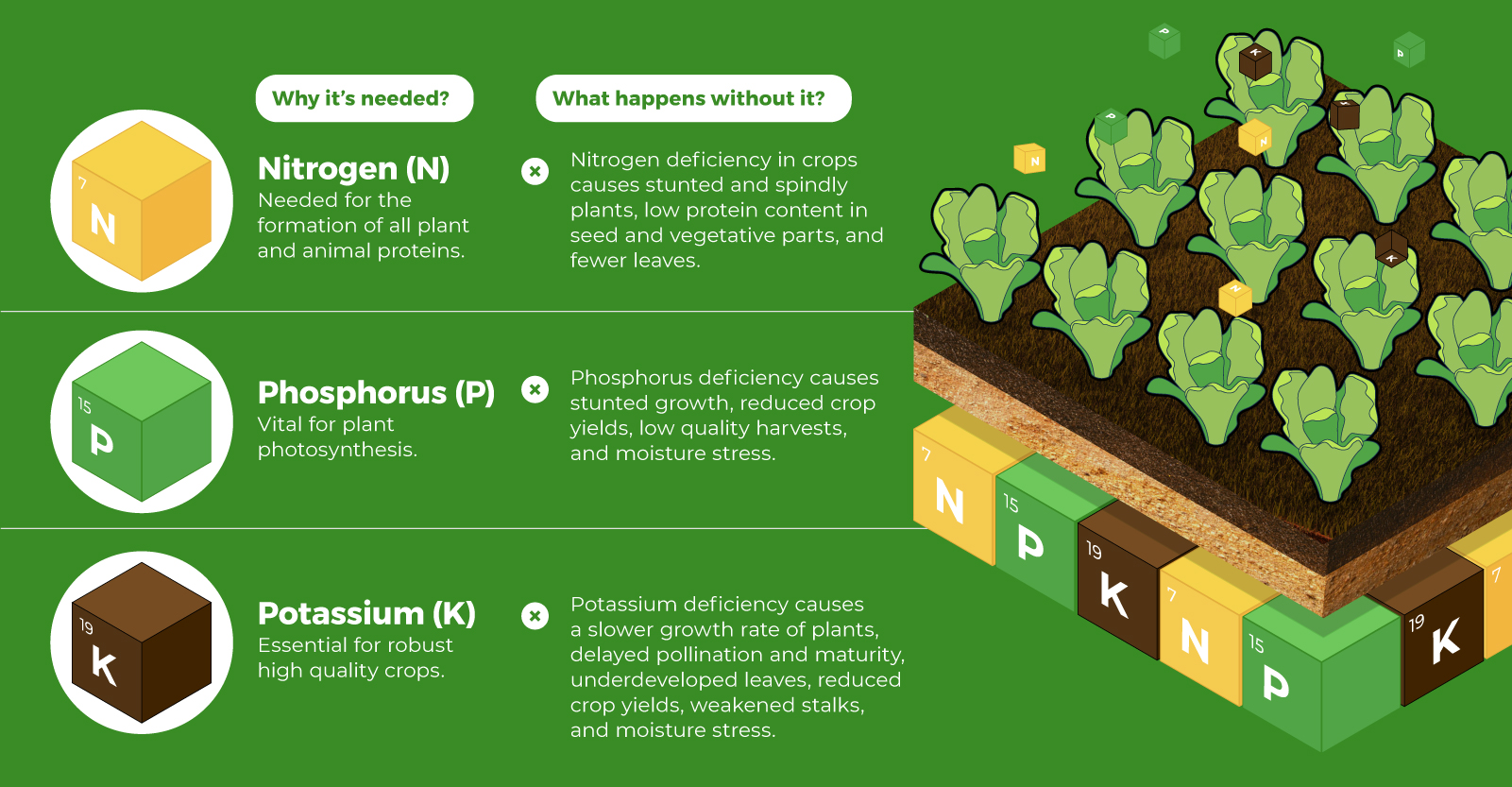
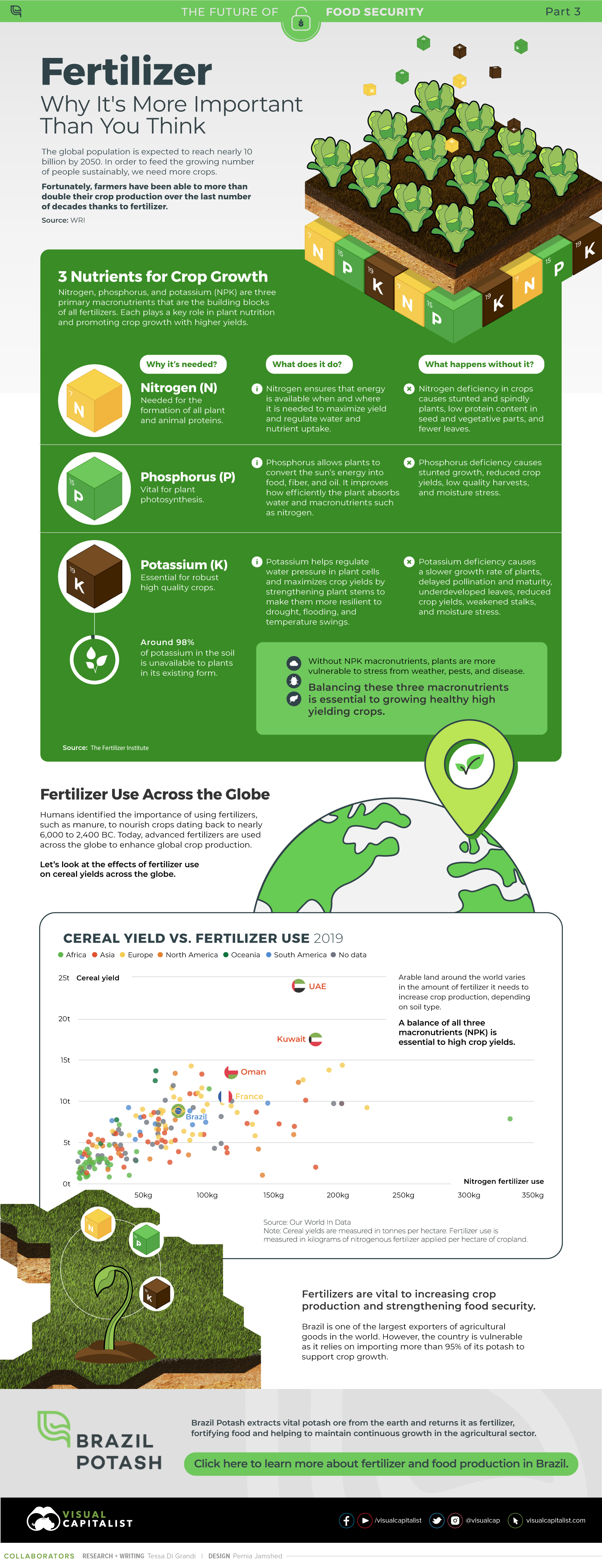
Food for Growth
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields. Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth. If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC. As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production. There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs. Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world. Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth. Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security. Click here to learn more about fertilizer and food production in Brazil.