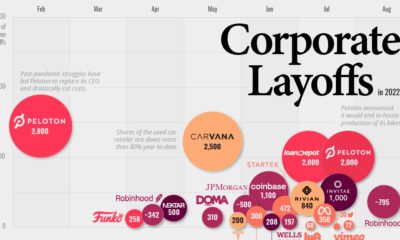
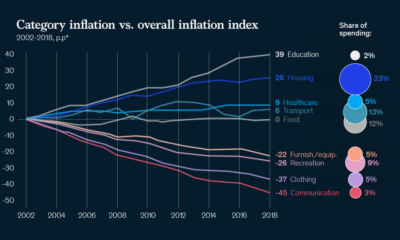
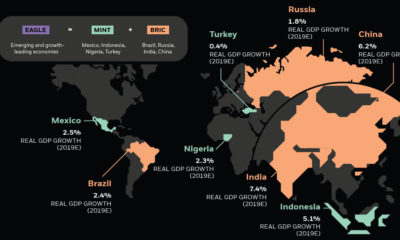
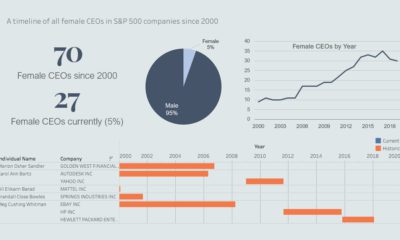
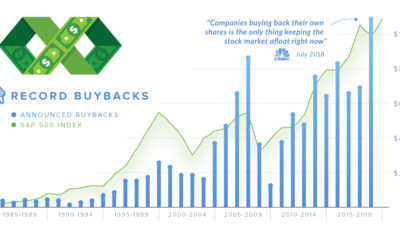
If today’s infographic looks familiar, that’s because it originates from a well-circulated report that Oxfam International puts together to show consolidation in the mass consumer goods industry. We are sharing it because we believe it is important for you to be aware of who is supplying the different brands and goods served on your dinner table.
Unlikely Links
The illusion of choice does not arise from the products we expect the companies to sell. We inherently know that PepsiCo sells plenty of beverages, including its flagship product. We know that Nestlé makes Kit Kat, Nesquick chocolate syrup, Nespresso coffee machines, and Nescafé instant coffee. What is less obvious is that Nestlé makes Gerber baby food, Hot Pockets, DiGiorno pizzas, and Stouffer brand frozen foods. Nestlé even owns two competing brands of fancy, carbonated water: San Pellegrino and Perrier. In fact, Nestlé has at least 29 brands with annual sales over $1 billion. The company literally has hundreds of different products in sectors ranging from pet food to soups and sauces. It’s the world’s largest food company by revenues, and it’s worth a whopping $240 billion in market capitalization.
They Might Be Giants
It’s not just Nestlé that is mind-boggling in size and scope. Other companies such as Coca-Cola, Kellogg’s, Mondelēz, PepsiCo, General Mills, Danone, and Mars are also massive. They each own dozens of brands that dominate certain product categories. Want to buy crackers? Pick up some Ritz, Triscuits, Wheat Thins, Air Crisps, or Premium brand crackers – but know they are all owned by Mondelēz (formerly Kraft Foods). Buying a chocolate bar? There are seemingly hundreds to choose from, but its just the illusion of choice. They pretty much all come from Mars, Nestlé, or Mondelēz (which owns Cadbury). There’s nothing wrong in buying from these brands, but remember that each dollar of your money is a vote. Vote for products and companies you believe in! Note: the above graphic is about 1.5 years old, and it misses recent acquisitions or changes in brand ownership. For example, Power Bar is now owned by Post Holdings, another giant consumer foods conglomerate. That said, we believes the point of the graphic still comes across. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.