In the U.S., the Fed hiked interest rates seven times. Globally, central banks raised interest rates for the first time in years in order to combat surging inflation. The Russian invasion of Ukraine and China’s COVID Zero ambitions threw markets and supply chains into further disarray. To recap the past 12 months, we’ve created an augmented version of the classic FinViz treemap, showing the final numbers posted for major U.S.-listed companies, sorted by sector and industry. Below, we look closer at the majority of companies that finished the year in the red, and the few industries and companies that beat the odds and saw positive growth.
The Winners
In this year’s stock market visualization, there’s a lot more red than green. That said, there were winners to be found, even during this turbulent year. Here are a few of them:
Energy
Looking at the visualization above, it’s easy to see which sector dominated this year. In fact, energy was the only sector to see positive performance, with most major energy stocks seeing double-digit growth. In particular, ExxonMobil had a monster year. The energy giant’s record Q3 profit came close to matching Apple’s (no small feat), and the company reportedly gave out hefty salary bumps and stock options to staff. This success didn’t go unnoticed as Exxon, and industry peers like Chevron, were excoriated for setting profit records while consumers felt the squeeze at the gas pump.
Healthcare (Sort of)
The healthcare sector was a mixed bag this year, but some winners did emerge. Large cap pharmaceutical companies managed to stay strong, even as the markets languished. Merck led the way with +45% growth this year, with Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, and Eli Lilly (+32%) also posting double-digit growth. For the latter two companies, this is a continuation of a long-term trend. Over the past decade, AbbVie is up over 600%, and Eli Lilly is up more than 800%. Pfizer (-12%) is the notable red spot in a green industry. The company had such a strong couple of years that the decline in 2022 is not surprising. It’s worth noting that the company still has billions in cash, and its oral antiviral tab could become a big sales driver over the coming year. The big three companies in the medical distribution industry—McKesson (+50%), Cardinal (+47%), and AmerisourceBergen (+24%)—also had a solid year.
Big Aerospace and Defense Companies
Major defense and aerospace stocks—with the exception of Boeing—outperformed the broader market in 2022. Lockheed Martin (+38%) capped off a strong year with a cool half a billion dollar contract from the U.S. Government.
The Losers
2022 was the worst year for the S&P 500 since the 2008 financial crisis. While the markets usually finish up, down years can happen. Last year was one of those rare times. Unlike the winning side of the equation, there’s no lack of material to cover in this section. We’ve scanned the sea of red for sectors to dig into.
Technology
The tech sector, from semiconductors to software, saw steep declines across the board last year. The list below, which shows the largest declines in the S&P 500, puts into perspective just how much value was wiped out in the tech sector this year. In absolute terms, Apple is the biggest loser on the year, shedding $846 billion from its market cap. Meta, which is in the midst of building out its vision for a “metaverse”, also saw one of the biggest declines, shedding $464 billion in market cap. Semiconductor stocks, like NVIDIA (-50%) and TSMC (-38%) were hit particularly hard. The so-called crypto winter, collapse of NFT transactions, and even bigger collapse of FTX, spelled tough times for any company that specialized in crypto. Although Coinbase avoided any major controversies last year, its stock was still hammered, falling 86% on the year.
Automakers
Last year posed many challenges for U.S. automakers. Macroeconomic issues aside, simply being able to roll new vehicles off the assembly line proved to be a challenge as supply chain issues persisted. Tesla saw 40% growth in deliveries last year, but that was not enough to satisfy investors. The automaker’s stock has been plummeting since September, and eventually finished down 65% on the year. Other pure-play EV companies fared even worse. Rivian and Lucid saw massive 90%+ declines over the course of last year.
Real Estate
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) stocks trailed the overall market due to soaring interest rates and uncertain economic circumstances. This was in stark contrast to 2021, when REITs had one of their best-ever performances. Though most of this sector is made up of REITs, WeWork is also in the mix. The previously high-flying company saw one of the steepest declines, finishing the year down more than 80%.
The Year Ahead
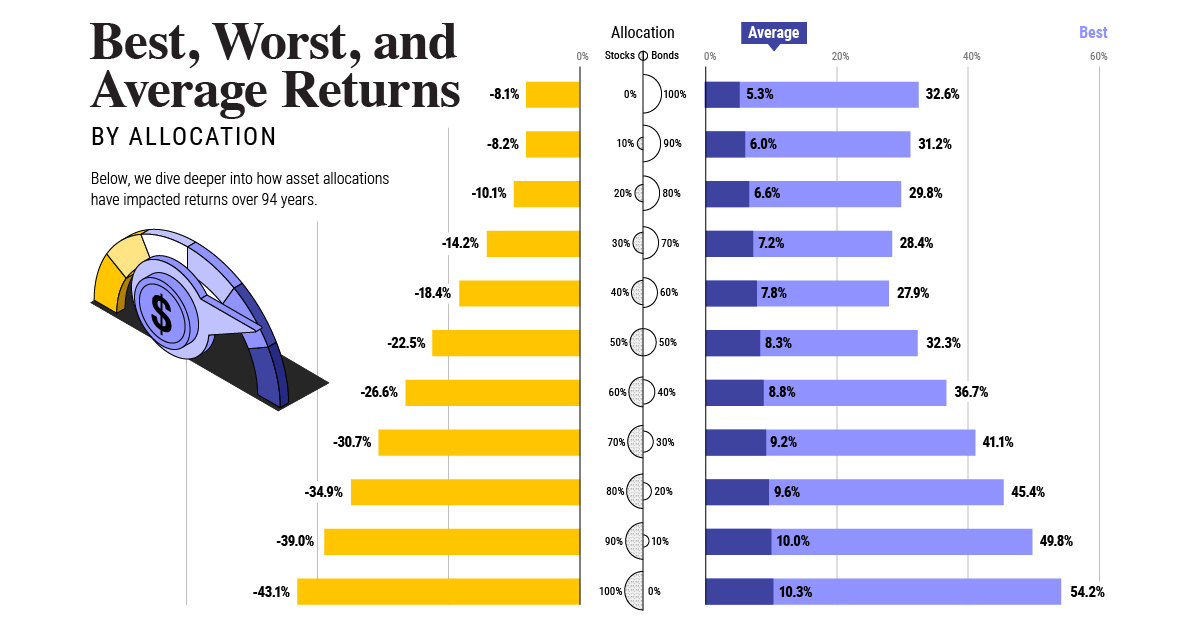
Many experts believe that a recession is coming, with severity and duration being the main topics of debate. Other questions remain as well. Will the tech sector continue mass layoffs going into 2023? Will supply chain issues persist? Will offices slowly spring back to life, or has remote work drastically altered the commercial real estate equation? Will the conflict in Ukraine continue, or come to a resolution? If there’s one thing we’ve learned over the past three years, it’s that predicting the future is anything but easy. on Last year, stock and bond returns tumbled after the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates at the fastest speed in 40 years. It was the first time in decades that both asset classes posted negative annual investment returns in tandem. Over four decades, this has happened 2.4% of the time across any 12-month rolling period. To look at how various stock and bond asset allocations have performed over history—and their broader correlations—the above graphic charts their best, worst, and average returns, using data from Vanguard.
How Has Asset Allocation Impacted Returns?
Based on data between 1926 and 2019, the table below looks at the spectrum of market returns of different asset allocations:
We can see that a portfolio made entirely of stocks returned 10.3% on average, the highest across all asset allocations. Of course, this came with wider return variance, hitting an annual low of -43% and a high of 54%.
A traditional 60/40 portfolio—which has lost its luster in recent years as low interest rates have led to lower bond returns—saw an average historical return of 8.8%. As interest rates have climbed in recent years, this may widen its appeal once again as bond returns may rise.
Meanwhile, a 100% bond portfolio averaged 5.3% in annual returns over the period. Bonds typically serve as a hedge against portfolio losses thanks to their typically negative historical correlation to stocks.
A Closer Look at Historical Correlations
To understand how 2022 was an outlier in terms of asset correlations we can look at the graphic below:
The last time stocks and bonds moved together in a negative direction was in 1969. At the time, inflation was accelerating and the Fed was hiking interest rates to cool rising costs. In fact, historically, when inflation surges, stocks and bonds have often moved in similar directions. Underscoring this divergence is real interest rate volatility. When real interest rates are a driving force in the market, as we have seen in the last year, it hurts both stock and bond returns. This is because higher interest rates can reduce the future cash flows of these investments. Adding another layer is the level of risk appetite among investors. When the economic outlook is uncertain and interest rate volatility is high, investors are more likely to take risk off their portfolios and demand higher returns for taking on higher risk. This can push down equity and bond prices. On the other hand, if the economic outlook is positive, investors may be willing to take on more risk, in turn potentially boosting equity prices.
Current Investment Returns in Context
Today, financial markets are seeing sharp swings as the ripple effects of higher interest rates are sinking in. For investors, historical data provides insight on long-term asset allocation trends. Over the last century, cycles of high interest rates have come and gone. Both equity and bond investment returns have been resilient for investors who stay the course.