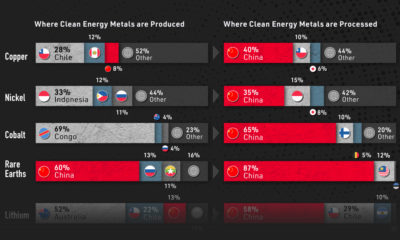
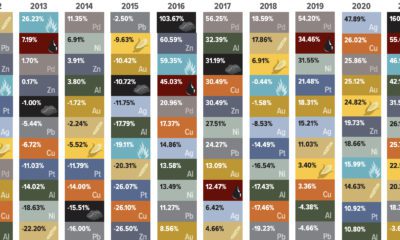
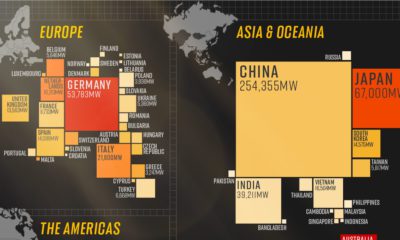
Tintina Resources Inc. (“the Company”) is a growth company focused on the exploration and development of base and precious metal projects in North America. The Company’s experienced management team has assembled an impressive portfolio of base metal projects in Alaska, including the Baird copper-zinc project, located 100 kilometers southeast of Red Dog, the world’s largest zinc producing mine, and the Black Butte Copper a copper-cobalt-silver project located in central Montana. The Company is currently focusing on advancing it’s flagship property, the Black Butte Copper Project, towards production.
CAUTIONARY NOTE:
This presentation of Tintina Resources Inc. (the “Company”) includes certain disclosure, including statements regarding the Company’s plans for and intentions with respect to exploration of the Company’s properties and other information which constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and Canadian securities legislation. The Company’s forward looking statements reflect the beliefs, opinions and projections on the date the statements are made. Forward-looking statements involve various risks and uncertainties. There can be no assurance that such statements will prove to be accurate, and actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. In making the forward-looking statements, the Company has applied certain factors and assumptions that the Company believes are reasonable, including that the Company is able to obtain any required government or other regulatory approvals and any required financing to complete the Company’s planned exploration activities, that the Company is able to procure equipment and supplies in sufficient quantities and on a timely basis and that actual results of exploration activities are consistent with management’s expectations. However, the forward looking statements are subject to numerous risks, uncertainties and other important factors relating to the Company’s operation as a mineral exploration company that may cause future results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in such forward-looking statements. Such important factors, uncertainties and risks may cause and include, among others, actual results of the Company’s exploration activities being materially different than those expected by management, uncertainties involved in the interpretation of drilling results and geological tests, and the estimation of reserves and resources, the need for cooperation of government agencies and native groups in the development of the Company’s properties, the need to obtain permits and governmental approvals, risks of operations such as accidents, equipment breakdowns, bad weather, non-compliance with environmental and permit requirements, unanticipated variations in geological structures, ore grades or recovery rates, unexpected cost increases, fluctuations in metal prices and currency exchange rates, delays in obtaining required government or other regulatory approvals or availability of financing in the debt and/or capital markets, inability to procure equipment and supplies in sufficient quantities and on a timely basis. Further, all statements, other than statements of historical fact, included herein including, without limitation, statements regarding anticipated completion of engineering studies, potential results of drilling and assays, timing of permitting, construction and production and other milestones, and the Company’s future operating or financial performance are forward-looking statements. Estimates of reserves and resources are also forward-looking statements in that they involve estimates of the mineralization that would be encountered, based on interpretation of drilling results and certain assumptions, if a deposit were developed and mined. There can be no assurance that such statements will prove to be accurate, and actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. The Company does not intend, and expressly disclaims any intention or obligation to, update or revise any forward-looking statements whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. – See more at: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/portfolio/tintina-resources-company-snapshot#sthash.acAiBgze.dpuf
on
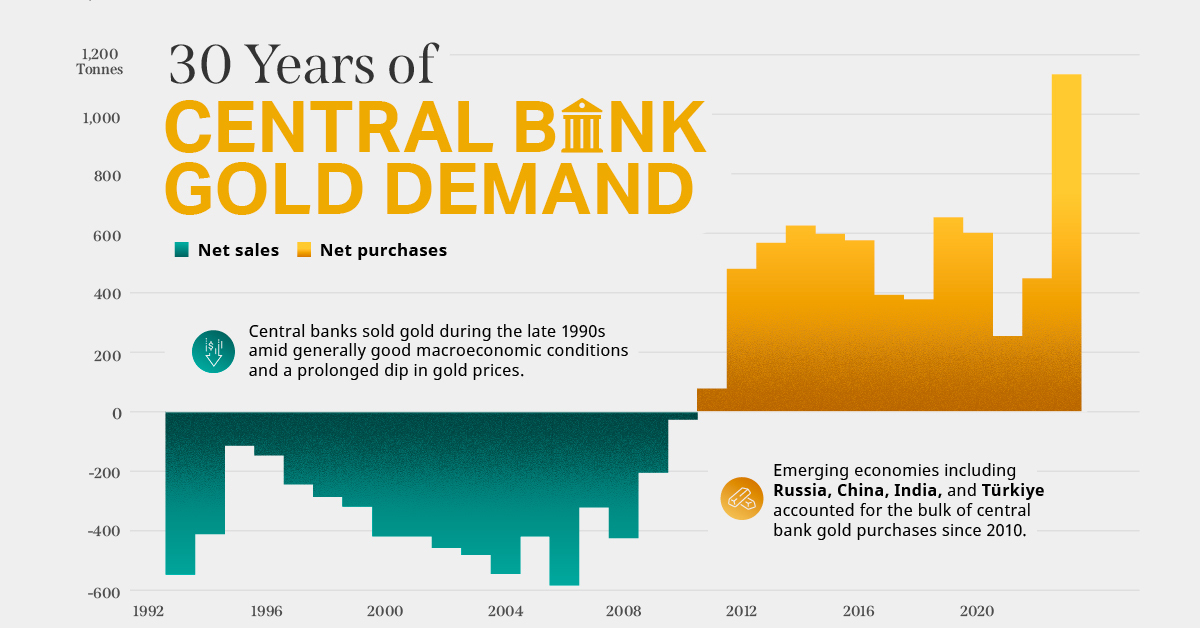
Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks?
Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967.
However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold.
The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.