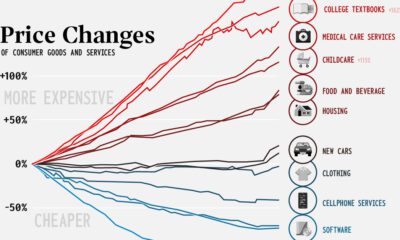
In this visual, we showcase select items and how inflation has impacted the price year-over-year. Additionally, we’ve charted the overall price increases across the overarching goods categories, using data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Note: These numbers are assessed using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for all Urban Consumers (CPI-U), using the U. S. city average by detailed expenditure category.
How Much has the Cost of Goods Gone Up?
Inflation has caused the cost of many goods to increase significantly compared to last year. The most dramatically affected item is elementary school lunches, a cost in the U.S. that is already unaffordable for many families. Here’s a look at every single reported good’s change in price from last year: School lunches became more expensive this year as a federal waiver program came to an end. The program had provided every school child in the country with free lunches. After school lunches, fuel oil and eggs rank high in terms of big jumps in their prices, increasing by 66% and 49% respectively. Some other notable increases: airfares have gone up by 36%, living room, kitchen, and dining room furniture by 10.3%, and alcoholic beverages at home by 4.5%. However, a number of goods have actually gone down in the index, including:
Smartphones: -23% Televisions: -17% Uncooked beef roasts: -8% Admission to sporting events: -7% Car and truck rentals: -6%
Interestingly, smartphones are not actually getting cheaper, rather the BLS adjusts for products that improve rapidly in quality year-over-year. Usually, most items are identical on a year-to-year basis, but smartphones are improving in their quality, which is why their price appears to be deflating rather than inflating.
U.S. Inflation
Overall, the items in the basket of goods under the Consumer Price Index have increased by a collective 7.1% since last year, making purchasing necessary food and energy items more difficult. Here’s another look at how each overarching category increased, between November 2021 and November 2022:
Food: +10.6% Energy: +13.1% All other items excluding food and energy: +6.0%
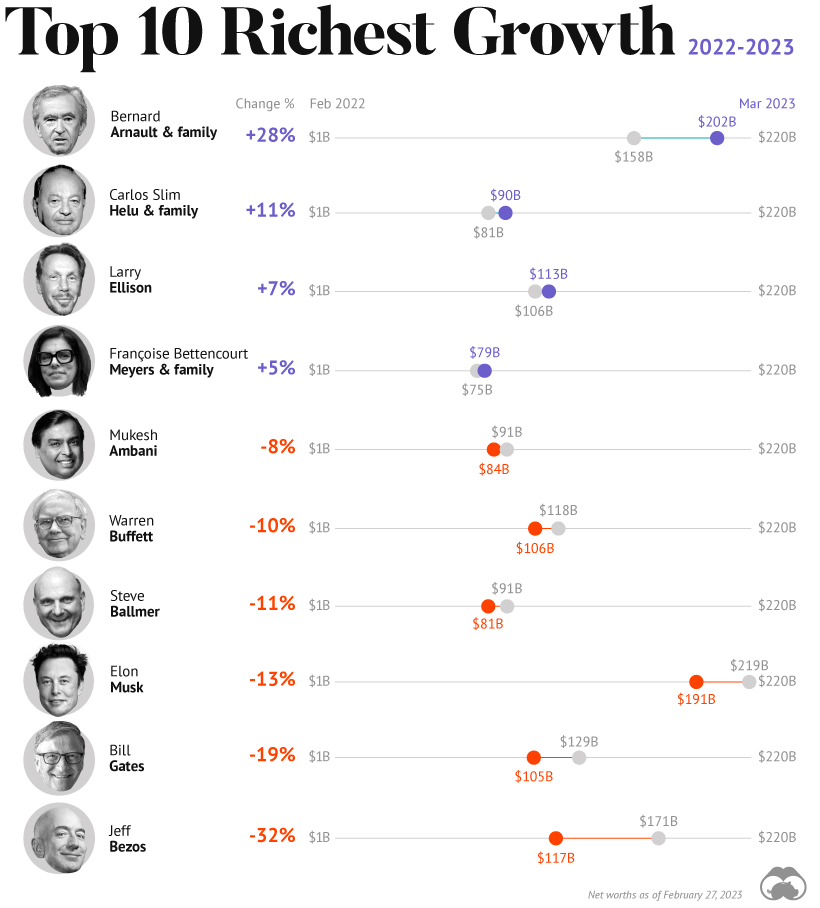
Purchasing your everyday ingredients to cook with, energy to heat your home, and all other items that are standard in our everyday lives has become increasingly expensive. In an effort to counter inflation pressures, the U.S. Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates to make borrowing more difficult in order to push down demand. Heading into 2023, many feel that a recession is on the way, and a lot of households will have to continue borrowing at higher rates to keep up with basic goods purchases. On the upside, some experts anticipate that although there will be economic downturn, it will be brief and won’t deeply impact the economy like past ones. on A lagging stock market dented these fortunes against high interest rates, energy shocks, and economic uncertainty. But some of the world’s billionaires have flourished in this environment, posting sky-high revenues in spite of inflationary pressures. With data from Forbes Real-Time Billionaires List, we feature a snapshot of the richest people in the world in 2023.
Luxury Mogul Takes Top Spot
The world’s richest person is France’s Bernard Arnault, the chief executive of LVMH.
With 75 brands, the luxury conglomerate owns Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, and Tiffany. LVMH traces back to 1985, when Arnault cut his first major deal with the company by acquiring Christian Dior, a firm that was struggling with bankruptcy.
Fast-forward to today, and the company is seeing record profits despite challenging market conditions. Louis Vuitton, for instance, has doubled its sales in four years.
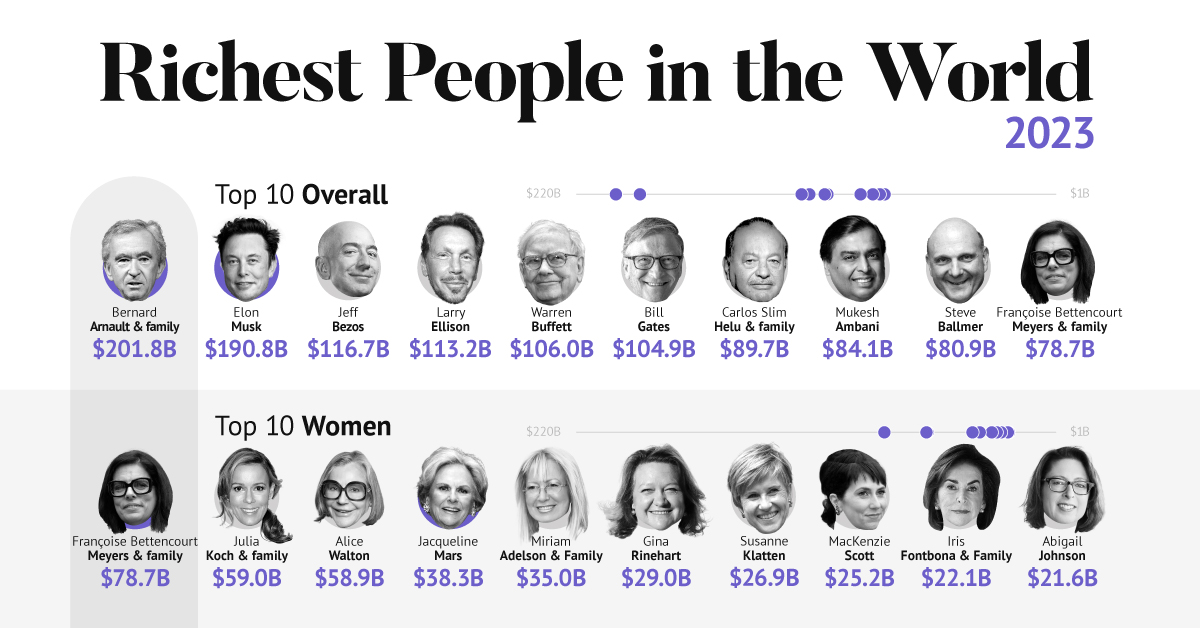
In the table below, we show the world’s 10 richest people with data as of February 27, 2023:
Elon Musk, the second-wealthiest person in the world has a net worth of $191 billion. In October, Musk took over Twitter in a $44 billion dollar deal, which has drawn criticism from investors. Many say it’s a distraction from Musk’s work with Tesla.
While Tesla shares have rebounded—after falling roughly 70% in 2022—Musk’s wealth still sits about 13% lower than in March of last year.
Third on the list is Jeff Bezos, followed by Larry Ellison. The latter of the two, who founded Oracle, owns 98% of the Hawaiian island of Lanai which he bought in 2012 for $300 million.
Fifth on the list is Warren Buffett. In his annual letter to shareholders, he discussed how Berkshire Hathaway reported record operating profits despite economic headwinds. The company outperformed the S&P 500 Index by about 22% in 2022.
How Fortunes Have Changed
Given multiple economic crosscurrents, billionaire wealth has diverged over the last year. Since March 2022, just four of the top 10 richest in the world have seen their wealth increase. Two of these are European magnates, while Carlos Slim Helu runs the largest telecom firm in Latin America. In fact, a decade ago Slim was the richest person on the planet. Overall, as the tech sector saw dismal returns over the year, the top 10 tech billionaires lost almost $500 billion in combined wealth.
Recent Shakeups in Asia
Perhaps the most striking news for the world’s richest centers around Gautam Adani, formerly the richest person in Asia. In January, Hindenburg Research, a short-selling firm, released a report claiming that the Adani Group engaged in stock manipulation and fraud. Specifically, the alleged the firm used offshore accounts to launder money, artificially boost share prices, and hide losses. The Adani Group, which owns India’s largest ports—along with ports in Australia, Sri Lanka, and Israel—lost $100 billion in value in the span of a few weeks. Interestingly, very few Indian mutual funds hold significant shares in Adani Group, signaling a lack of confidence across India’s market, which was also cited in Hindenburg’s report. As a result, Mukesh Ambani has climbed to Asia’s top spot, controlling a $84 billion empire that spans from oil and gas and renewable energy to telecom. His conglomerate, Reliance Industries is the largest company by market cap in India.