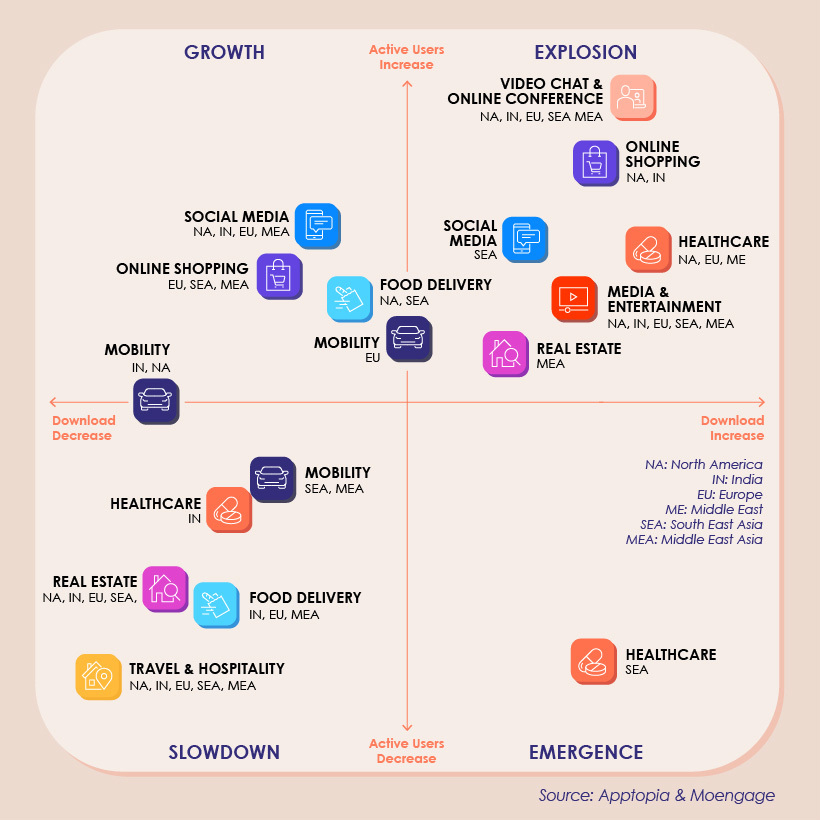
With the physical world now slowly receding, consumers are suddenly more reliant on apps for communication, shopping, staying healthy, and entertainment. Today’s graphic pulls data from a new report by MoEngage and Apptopia, and it plots the winners and losers of the pandemic from the app world in North America.
Embracing the App Economy with Open Arms
Consumers are looking for different ways to manage their lives while in lockdown, and in some cases, apps could provide the perfect solution. In fact, people spent 20% more time using apps in the first quarter of 2020 compared to 2019. During that time, consumers also spent over $23 billion in app stores—the largest spend per quarter recorded to date. While consumers across the globe lean on apps to support them in times of crisis, what exactly are consumers in North America using?
Climbing to the Top
Given the sheer volume of people working remotely, it’s no surprise to see video chat and online conference apps experiencing explosive growth. In North America, these apps witnessed an astronomical 627% increase in downloads, and a 121% increase in daily active users (DAUs). Video conferencing app Zoom expanded its worldwide user base by 300% in just under a month. Upwards of 500 participants can attend a meeting at any one time, hence why it has become a popular option for virtual conferences, festivals and even religious sermons. As we adapt to life indoors, the Zoom boom shows no signs of slowing, even despite the app’s recent data privacy and security scandal.
Slowing to a Standstill
Unfortunately, indoor living is not conducive to globetrotting. As travel and hospitality app downloads in North America decline by 12%, this is the harsh reality that the industry needs to come to terms with for the foreseeable future. Interestingly, airlines in the U.S. did not see a reduction in app downloads until early March, which may be attributed to the later timing of the COVID-19 shutdowns as in comparison to other countries around the world. In the short-term rentals space, Airbnb has experienced a drastic decline in bookings, and is adopting new cleaning protocols in an attempt to appease both hosts and guests. The tech company has since lowered its internal evaluation, from $31 billion to $26 billion, which could disrupt the company’s plan to go public in 2020.
Emerging Victorious
Because the largest social media networks already boast a significantly large audience, new downloads is not necessarily a metric that could make or break this cohort. Instead, DAUs are a much better indicator of success, and from what the report suggests, people have become more devoted to these platforms.
For U.S. adults, social media usage jumped from 20% of total mobile app usage in the early part of the year, to 25% in mid-March. In fact, between January and March, daily active users on Instagram and Facebook rose to 127 million and 195 million, respectively.
Measuring the Global Impact
When we look at the popularity of apps across different parts of the world, some interesting observations appear. First of all, healthcare apps in South East Asia are categorized as emerging—meaning they show promise, but have minimal active users.
Although DAUs of healthcare apps in South East Asia are declining, fascinatingly, there has been a 110% increase in spend on these apps during the outbreak. The report suggests that this could be attributed to the user base becoming more loyal as a result of trust-building advertising campaigns in this space. Real estate is a sector seeing a simultaneous increase and decrease in users worldwide. In Middle-East Asia for instance, these apps are exploding in popularity, but in other parts of the world they are experiencing a slowdown. This could be due to restrictions in certain parts of the world slowly starting to lift.
An Unsung Hero
Technology is becoming an increasingly divisive topic. Data security scandals, the spread of false information, and its impact on mental health are just some of the reasons why technology’s role in society regularly comes into question. However, it has allowed us to remain connected in a time of crisis, and has also been pivotal in facilitating the spread of reliable information during lockdown. If anything, the pandemic has shown us how vulnerable we are without technology—and how instrumental apps are in keeping us busy, informed, and sane. on The leading options for preventing infection include social distancing, mask-wearing, and vaccination. They are still recommended during the upsurge of the coronavirus’s latest mutation, the Omicron variant. But in December 2021, The United States Food and Drug Administration (USDA) granted Emergency Use Authorization to two experimental pills for the treatment of new COVID-19 cases. These medications, one made by Pfizer and the other by Merck & Co., hope to contribute to the fight against the coronavirus and its variants. Alongside vaccinations, they may help to curb extreme cases of COVID-19 by reducing the need for hospitalization. Despite tackling the same disease, vaccines and pills work differently:
How a Vaccine Helps Prevent COVID-19
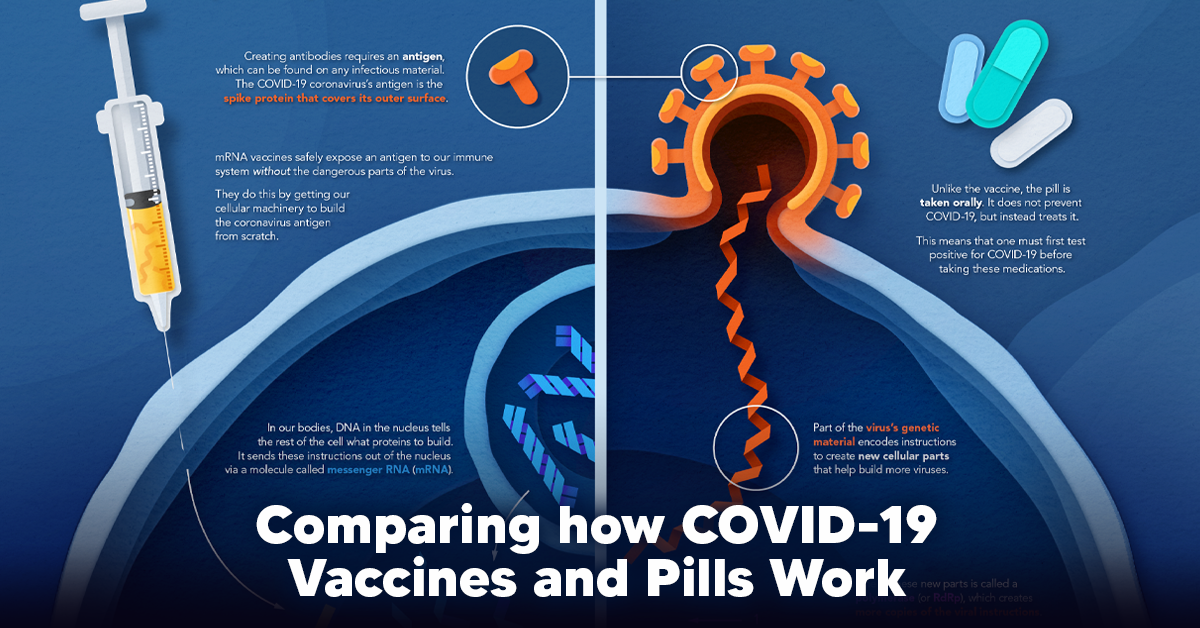
The main purpose of a vaccine is to prewarn the body of a potential COVID-19 infection by creating antibodies that target and destroy the coronavirus. In order to do this, the immune system needs an antigen. It’s difficult to do this risk-free since all antigens exist directly on a virus. Luckily, vaccines safely expose antigens to our immune systems without the dangerous parts of the virus. In the case of COVID-19, the coronavirus’s antigen is the spike protein that covers its outer surface. Vaccines inject antigen-building instructions* and use our own cellular machinery to build the coronavirus antigen from scratch. When exposed to the spike protein, the immune system begins to assemble antigen-specific antibodies. These antibodies wait for the opportunity to attack the real spike protein when a coronavirus enters the body. Since antibodies decrease over time, booster immunizations help to maintain a strong line of defense. *While different vaccine technologies exist, they all do a similar thing: introduce an antigen and build a stronger immune system.
How COVID Antiviral Pills Work
Antiviral pills, unlike vaccines, are not a preventative strategy. Instead, they treat an infected individual experiencing symptoms from the virus. Two drugs are now entering the market. Merck & Co.’s Lagevrio®, composed of one molecule, and Pfizer’s Paxlovid®, composed of two. These medications disrupt specific processes in the viral assembly line to choke the virus’s ability to replicate.
The Mechanism of Molnupiravir
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) is a cellular component that works similar to a photocopying machine for the virus’s genetic instructions. An infected host cell is forced to produce RdRp, which starts generating more copies of the virus’s RNA. Molnupiravir, developed by Merck & Co., is a polymerase inhibitor. It inserts itself into the viral instructions that RdRp is copying, jumbling the contents. The RdRp then produces junk.
The Mechanism of Nirmatrelvir + Ritonavir
A replicating virus makes proteins necessary for its survival in a large, clumped mass called a polyprotein. A cellular component called a protease cuts a virus’s polyprotein into smaller, workable pieces. Pfizer’s antiviral medication is a protease inhibitor made of two pills: With a faulty polymerase or a large, unusable polyprotein, antiviral medications make it difficult for the coronavirus to replicate. If treated early enough, they can lessen the virus’s impact on the body.
The Future of COVID Antiviral Pills and Medications
Antiviral medications seem to have a bright future ahead of them. COVID-19 antivirals are based on early research done on coronaviruses from the 2002-04 SARS-CoV and the 2012 MERS-CoV outbreaks. Current breakthroughs in this technology may pave the way for better pharmaceuticals in the future. One half of Pfizer’s medication, ritonavir, currently treats many other viruses including HIV/AIDS. Gilead Science is currently developing oral derivatives of remdesivir, another polymerase inhibitor currently only offered to inpatients in the United States. More coronavirus antivirals are currently in the pipeline, offering a glimpse of control on the looming presence of COVID-19. Author’s Note: The medical information in this article is an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please talk to your doctor before undergoing any treatment for COVID-19. If you become sick and believe you may have symptoms of COVID-19, please follow the CDC guidelines.